目录
基础
频率
散列
-
选择散列函数
-
Division method
- $h(k)=k \mod m$
-
Multiplication method
-
$m=2^r$,计算机有$w$位词
- $h(k)=(A\cdot k\mod 2^w)\rm{rsh}(w-r)$
- 模块轮 (Modular wheel):将轮子旋转$k$个$A$,然后舍弃最后几位
-
http://www.alloyteam.com/2017/05/hash-functions-introduction/
加法、位运算、乘法、除法、查表、混合
一个好的哈希函数应该具备以下三点:
- 抗碰撞性,尽量避免冲突。
- 抗篡改性,只要改动一个字节,其哈希值也会很大不同。
- 查找效率。
-
-
处理冲突
-
拉链法
填装因子$\alpha=表中记录数(键数)n/散列表长度(槽数)m$
不成功搜索的期望时间$=\Theta(1+\alpha)$
-
开放定址法:线性探查法、平方探查法、再散列法、伪随机序列法
假设均匀散列,每个键等可能地将$m!$种排序之一作为其探查序列。
定理:不成功搜索的期望探查次数 $E[$#$probes]\le1/(1-\alpha)$
-
B树和B+树
王道数据结构P243 B树和B+树
-
B树
一棵$m$阶B树或为空树,或为满足如下特征的$m$叉树:
-
树中每个结点至多有$m$棵子树(即至多含有$m-1$个关键字)。
-
若根节点不是终端结点,则至少有2棵子树。
-
除根结点外的所有非叶结点至少有$\lceil m/2\rceil$棵子树(即至少含有$\lceil m/2\rceil-1$个关键字)
-
所有的非叶结点的结构:$n,P_0,K_1,P_1,K_2,P_2,…,K_n,P_n$. 其中$K_i$为结点的关键字,且满足$K_1\lt K_2\lt…\lt K_n$; $P_i$所指子树中所有结点的关键字均大于$K_i$, $n$为结点中关键字的个数。
-
所有的叶节点都出现再同一层次上,并且不带信息。
B树的插入:定位(找到最底层的某个非叶结点),插入(分裂上移)
B树的删除:不在终端结点删除(删除合并),在终端结点删除(兄弟够借,兄弟不够借)
-
-
B+树
$m$阶B+树与$m$阶B树的主要差异在于:
-
在B+树中,具有$n$个关键字的结点只含有$n$棵子树,即每个关键字对应一棵子树;而在B树中,具有$n$个关键字的结点含有$(n+1)$棵子树。
-
在B+树中,每个结点(非根内部结点)关键字个数$n$的范围时$\lceil m/2\rceil \le n \le m$(根结点:$1\le n\le m-1$);在B树中,每个结点(非根内部结点)关键字个数$n$的范围是$\lceil m/2\rceil-1 \le n \le m-1$(根结点:$1\le n\le m-1$)。
-
在B+树中,叶结点包含信息,所有非叶节点仅起到索引作用,非叶结点中的每个索引项只含有对应子树的最大关键字和指向该子树的指针,不含有该关键字对应记录的存储地址。
-
在B+树中,叶结点包含了全部关键字,即在非叶结点中出现的关键字也会出现在叶结点中;而在B树中,叶结点包含的关键字和其他结点包含的关键字是不重复的。
-
布隆过滤器
什么是布隆过滤器
布隆过滤器(Bloom Filter)是一个叫做 Bloom 的老哥于1970年提出的。我们可以把它看作由二进制向量(或者说位数组)和一系列随机映射函数(哈希函数)两部分组成的数据结构。相比于我们平时常用的的 List、Map 、Set 等数据结构,它占用空间更少并且效率更高,但是缺点是其返回的结果是概率性的,而不是非常准确的。理论情况下添加到集合中的元素越多,误报的可能性就越大。并且,存放在布隆过滤器的数据不容易删除。
布隆过滤器的原理
当一个元素加入布隆过滤器中的时候,会进行如下操作:
- 使用布隆过滤器中的哈希函数对元素值进行计算,得到哈希值(有几个哈希函数得到几个哈希值)。
- 根据得到的哈希值,在位数组中把对应下标的值置为 1。
当我们需要判断一个元素是否存在于布隆过滤器的时候,会进行如下操作:
- 对给定元素再次进行相同的哈希计算;
- 得到值之后判断位数组中的每个元素是否都为 1,如果值都为 1,那么说明这个值在布隆过滤器中,如果存在一个值不为 1,说明该元素不在布隆过滤器中。
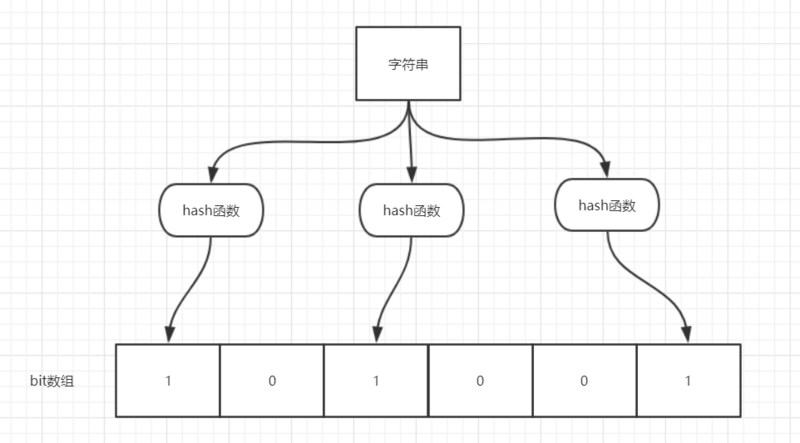
布隆过滤器说某个元素存在,小概率会误判。布隆过滤器说某个元素不在,那么这个元素一定不在。
布隆过滤器使用场景
- 判断给定数据是否存在:比如判断一个数字是否在于包含大量数字的数字集中(数字集很大,5亿以上!)、 防止缓存穿透(判断请求的数据是否有效避免直接绕过缓存请求数据库)、邮箱的垃圾邮件过滤、黑名单功能等等。
- 去重:比如爬给定网址的时候对已经爬取过的 URL 去重。
-
海量数据的TopK问题
- 找重复最多的TopK:散列成多个小数据集再统计
- 找最大TopK:外排、优先队列、分治找最大
- 去重:布隆过滤器
-
跳表
主方法
CLRS
对于形式$T(n)=aT(n/b)+f(n)$的递归,分为3种情况:
-
$f(n)=O(n^{\log_ba-\varepsilon})$
$f(n)$多项式地慢于$n^{\log_ba}$增长(相差$n^\varepsilon$)
结论:$T(n)=\Theta(n^{\log_ba})$
-
$f(n)=\Theta(n^{\log_ba}\log^kn)$
$f(n)$与$n^{\log_ba}$以相似速率增长
结论:$T(n)=\Theta(n^{\log_ba}\log^{k+1}n)$
-
$f(n)=\Omega(n^{\log_ba+\varepsilon})$
$f(n)$多项式地快于$n^{\log_ba}$增长(相差$n^\varepsilon$)
结论:$T(n)=\Theta(f(n))$
二分查找
-
一般的二分查找
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
int binarySearch(int n, int key) { int lo = 0; int hi = n - 1; while(lo <= hi) { int mid = (lo + hi) / 2; if(num[mid] < key) lo = mid + 1; else if(num[mid] > key) hi = mid - 1; else return mid; } return lo; }
-
找到第一个大于等于目标值的位置
解释:如果目标值大于中间数,在右半边查找;如果目标值小于等于中间数,在左半边查找。当目标值等于中间数时,将会放弃中间数在左半边查找,最后一次循环
lo == hi时,lo的值又会增1,所以可以找到等于目标值的第一个数。1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
int binarySearch(int n, int key) { int lo = 0; int hi = n - 1; while(lo <= hi) { int mid = (lo + hi) / 2; if(num[mid] < key) lo = mid + 1; else hi = mid - 1; } return lo; }
排序
-
插入排序:时间$O(n^2)$,空间$O(1)$,稳定
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
void insetionSort(int[] a, int N) { for(int i = 1; i < N; i++) { for(int j = i; j > 0 && a[j] < a[j-1]; j--) { exch(a, j, j-1); } } }
-
选择排序:时间$O(n^2)$,空间$O(1)$,不稳定
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
void selectionSort(int[] a, int N) { for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) { int min = i; for(int j = i+1; j < N; j++) { if(a[j] < a[min]) min = j; } exch(a, i, min); } }
-
冒泡排序:时间$O(N^2)$,空间$O(1)$,稳定
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
void bubleSort(int[] a, int N) { for(int i = 0; i < N-1; i++) { for(int j = N-1; j > i; j--) { if(a[j-1] > a[j]) exch(a, j-1, j); } } }
-
希尔排序(对比插入排序):时间$O(n^{1.3})$,最坏$O(n^2)$,空间$O(1)$,不稳定
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
void shellSort(int[] a, int N) { for(int h = N/2; h >= 1; h /= 2) { for(int i = h; i < N; i++) { for(int j = i; j >= h && a[j] < a[j-h]; j -= h) { exch(a, j, j-h); } } } }
-
归并排序:时间$O(n\log n)$,空间$O(n)$,稳定
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22
int[] aux = new int[N]; void mergeSort(int[] a, int lo, int hi) { if(hi <= lo) return; int mid = (lo + hi) / 2; mergeSort(a, lo, mid); mergeSort(a, mid+1, hi); merge(a, lo, mid, hi); } void merge(int[] a, int lo, int mid, int hi) { int i = lo, j = mid + 1; for(int k = lo; k <= hi; k++) { aux[k] = a[k]; } for(int k = lo; k <= hi; k++) { if(i > mid) a[k] = aux[j++]; else if(j > hi) a[k] = aux[i++]; else if(aux[j] < aux[i]) a[k] = aux[j++]; else a[k] = aux[i++]; } }
-
快速排序:时间$O(n\log n)$,最坏$O(n^2)$,空间$O(\log n)$,最坏$O(n)$,不稳定
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
void quickSort(int[] a, int lo, int hi) { if(hi <= lo) return; int j = partition(a, lo, hi); quickSort(a, lo, j-1); quickSort(a, j+1, hi); } int partition(int[] a, int lo, int hi) { int i = lo, j = hi+1; int pivot = a[lo]; while(true) { while(a[++i] < pivot) if(i == hi) break; while(pivot < a[--j]) if(j == lo) break; if(i >= j) break; exch(a, i, j); } exch(a, lo, j); return j; }
-
堆排序(大根堆)
删除堆顶元素:先将堆的最后一个元素与堆顶元素交换,再对此时的根结点进行sink操作。
插入:先将新结点放在堆的末端,再对这个新结点进行swim操作。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28
void heapSort(int[] a, int N) { // 建堆 for(int k = N/2; k >= 1; k--) { sink(a, k, N); } // 排序:不断删除堆顶元素,放到末尾 while(N > 1) { exch(a, 1, N--); sink(a, 1, N); } } void swim(int[] a, int k) { while(k > 1 && a[k/2] < a[k]) { exch(a, k/2, k); k /= 2; } } void sink(int[] a, int k, int N) { while(2*k <= N) { int j = 2*k; if(j < N && a[j] < a[j+1]) j++; if(a[k] >= a[j]) break; exch(a, k, j); k = j; } }
-
回溯
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
// Backtracking pseudocode bool Solve(configuration conf) { if (no more choices) // BASE CASE return (conf is goal state); for (all available choices) { try one choice c; // solve from here, if works out, you're done if (Solve(conf with choice c made)) return true; unmake choice c; } return false; // tried all choices, no soln found }
-
DFS
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
bool mark[]; void dfs(Graph G, int v) { marked[v] = true; for(int w: G.adj(v)) { if(!marked[w]) { dfs(G, w); } } } int main() { for(int s = 0; s < G.V(); s++) { if(!mark[s]) { dfs(G, s); } } return 0; }
-
BFS
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
void bfs(Graph G, int s) { queue<int> q; marked[s] = true; q.push(s); while(!q.empty()) { int v = q.front(); q.pop(); for(int w: G.adj(v)) { if(!marked[w]) { marked[w] = true; q.push(w); } } } }
-
并查集
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28
#include <cstdio> int tree[]; int findRoot(int x) { if(tree[x] == -1) return x; int ret = findRoot(tree[x]); tree[x] = ret; return ret; } int main() { for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) tree[i] = -1; while(m--) { int a, b; scanf("%d%d", &a, &b); a = findRoot(a); b = findRoot(b); if(a != b) tree[a] = b; } int res = 0; for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { if(tree[i] == -1) res++; } return 0; }
-
最小生成树(MST) Kruskal
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41
#include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> int tree[]; struct Edge { int a, b; int cost; bool operator < (const Edge& b) const { return cost < b.cost; } } edge[]; int findRoot(int x) { if(tree[x] == -1) return x; int ret = findRoot(tree[x]); tree[x] = ret; return ret; } int main() { for(int i = 0; i < n*(n-1)/2; i++) { scanf("%d%d%d", &edge[i].a, &edge[i].b, &edge[i].cost); } sort(edge, edge+n*(n-1)/2); for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { tree[i] = -1; } int res = 0; for(int i = 0; i < n*(n-1)/2; i++) { int a = findRoot(edge[i].a); int b = findRoot(edge[i].b); if(a != b) { tree[a] = b; res += edge[i].cost; } } printf("%d\n", res); return 0; }
-
Dijkstra 邻接表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55
#include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> #include <vector> const int INF = 0x7fffffff; struct Edge { int to; int cost; }; vector<Edge> edge[]; bool mark[]; int dist[]; int main() { for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { edge[i].clear(); mark[i] = false; dist[i] = -1; } for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { int a, b, c; scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c); Edge tmp; tmp.cost = c; tmp.to = b; edge[a].push_back(tmp); tmp.to = a; edge[b].push_back(tmp); } mark[1] = true; dist[1] = 0; int newPoint = 1; for(int i = 0; i < n-1; i++) { int len = edge[newPoint].size(); for(int j = 0; j < len; j++) { int to = edge[newPoint][j].to; int cost = edge[newPoint][j].cost; if(mark[to]) continue; if(dist[to] == -1 || dist[to] > dist[newPoint] + cost) dist[to] = dist[newPoint] + cost; } int min = INF; for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++) { if(mark[j]) continue; if(dist[j] == -1) continue; if(dist[j] < min) { min = dist[j]; newPoint = j; } } mark[newPoint] = true; } return 0; }
-
拓扑排序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32
class Solution { public: vector<int> findOrder(int numCourses, vector<vector<int>>& prerequisites) { vector<vector<int>> graph(numCourses, vector<int>()); vector<int> indegree(numCourses, 0); for(vector<int> prerequisite: prerequisites) { int start = prerequisite[1]; int end = prerequisite[0]; graph[start].push_back(end); indegree[end]++; } vector<int> res; queue<int> q; for(int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) { if(indegree[i] == 0) { q.push(i); } } while(!q.empty()) { int node = q.front(); res.push_back(node); q.pop(); for(int neighbour: graph[node]) { indegree[neighbour]--; if(indegree[neighbour] == 0) { q.push(neighbour); } } } return res.size()==numCourses? res: vector<int>(); } };
-
0-1背包
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29
#include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; int dp[]; struct List { int volume; int weight; } list[]; int main() { int v, n; scanf("%d%d", &v, &n); for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { scanf("%d%d", &list[i].volume, &list[i].weight); } for(int j = 0; j <= v; j++) { dp[j] = 0; } for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { for(int j = v; j >= list[i].volume; j--) { dp[j] = max(dp[j-list[i].volume] + list[i].weight, dp[j]); } } printf("%d\n", dp[v]); return 0; }
初始化分两种情况:
- 如果背包要求正好装满则初始化 f[0] = 0, f[1~w] = -INF;
- 如果不需要正好装满 f[0~v] = 0;
-
完全背包
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38
#include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; const int INF = 0x7fffffff; int dp[]; struct List { int volume; int weight; } list[]; int main() { int t; scanf("%d", &t); while(t--) { int a, b, n; scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &n); int v = b - a; for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { scanf("%d%d", &list[i].weight, &list[i].volume); } dp[0] = 0; for(int j = 1; j <= v; j++) { dp[j] = INF; } for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { for(int j = list[i].volume; j <= v; j++) { if (dp[j-list[i].volume] != INF) dp[j] = min(dp[j-list[i].volume] + list[i].weight, dp[j]); } } if(dp[v] == INF) printf("This is impossible.\n"); else printf("The minimum amount of money in the piggy-bank is %d\n", dp[v]); } return 0; }
-
最大公共子序列、最大公共子串
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
int dp[][] = new int[s1.length()+1][s2.length()+1]; for(int i = 1; i <= s1.length(); i++) { for(int j = 1; j <= s2.length(); j++) { if(s1.charAt(i-1) == s2.charAt(j-1)) dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1; //else dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1]); else dp[i][j] = 0; } } for(int i = 0; i <= s1.length(); i++) { for(int j = 0; j <= s2.length(); j++) { System.out.format("%d ", dp[i][j]); } System.out.println(); } System.out.println(dp[s1.length()][s2.length()]);
-
哈夫曼树
思路:将所有节点放到小顶堆里,每次拿出最小的两个节点,加起来放回堆里。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38
#include <cstdio> #include <queue> using namespace std; struct cmp { bool operator()(const int& a, const int& b) { return a > b; } }; priority_queue<int, vector<int>, cmp> pq; int main() { int n; while(scanf("%d", &n) != EOF) { while(n--) { int node; scanf("%d", &node); pq.push(node); } int a, b, res = 0; a = pq.top(); pq.pop(); b = pq.top(); pq.pop(); res += (a+b); while(!pq.empty()) { a = a + b; b = pq.top(); pq.pop(); res += (a+b); } printf("%d\n", res); } return 0; }
分治
leetcode 74: 搜索二维矩阵
-
题意:矩阵中行有序,后面一行的第一个数比前一行最后一个数大。
-
方法1:两次二分查找
-
思路:先二分查找到目标值可能在的那一行(比较方便的方法是找到最后一列大于等于目标值的那一行),然后二分查找那一行。
-
时间:$O(\log m+\log n)=O(\log mn)$
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34
class Solution { public: bool searchMatrix(vector<vector<int>>& matrix, int target) { // [] => 0 // [[]] => 0 if(matrix.size() == 0) return false; if(matrix[0].size() == 0) return false; // binary search row // <= int lo = 0; int hi = matrix.size() - 1; while(lo <= hi) { int mid = (lo + hi) / 2; if(matrix[mid][0] < target) lo = mid + 1; else hi = mid - 1; } if(lo < matrix.size() && matrix[lo][0] == target) return true; if(lo == 0) return false; int row = lo - 1; // binary search col // >= lo = 0; hi = matrix[row].size() - 1; while(lo <= hi) { int mid = (lo + hi) / 2; if(matrix[row][mid] < target) lo = mid + 1; else hi = mid - 1; } if(lo < matrix[row].size() && matrix[row][lo] == target) return true; return false; } };
-
-
方法2:一次二分查找
-
思路:直接当成一维数组进行二分查找。
-
时间:$O(\log mn)$
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
class Solution { public: bool searchMatrix(vector<vector<int>>& matrix, int target) { // [] => 0 // [[]] => 0 int rows = matrix.size(); if(rows == 0) return false; int cols = matrix[0].size(); if(cols == 0) return false; int lo = 0; int hi = rows * cols - 1; while(lo <= hi) { int mid = (lo + hi) / 2; if(matrix[mid/cols][mid%cols] < target) lo = mid + 1; else hi = mid - 1; } if(lo < rows * cols && matrix[lo/cols][lo%cols] == target) return true; return false; } };
-
leetcode 240: 搜索二维矩阵II
-
题意:矩阵中行有序列有序,查找目标值。
-
方法1:分治
-
思路:第4象限的数一定比中间值大,第3象限的数一定比中间值小,所以比较中间值与目标值的大小,可以将问题转化为3个子问题。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
zone 1 zone 2 * * * * | * * * * * * * * | * * * * * * * * | * * * * * * * * | * * * * ----------------------- * * * * | * * * * * * * * | * * * * * * * * | * * * * * * * * | * * * * zone 3 zone 4
- 时间:$T(mn)=3T(mn/4)+O(1)$,根据主方法,$T(mn)=\Theta((mn)^{\log_43})$.
- 参考
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33
class Solution { public: bool searchMatrix(vector<vector<int>>& matrix, int target) { if(matrix.empty()) return false; if(matrix[0].empty()) return false; int rows = matrix.size(); int cols = matrix[0].size(); return searchMatrix(matrix, target, 0, 0, rows-1, cols-1); } private: bool searchMatrix(vector<vector<int>>& matrix, int target, int loI, int loJ, int hiI, int hiJ) { cout << loI << " " << loJ << " " << hiI << " " << hiJ << endl; if(loI > hiI || loJ > hiJ) return false; if(loI == hiI && loJ == hiJ) return matrix[loI][loJ] == target; int midI = (loI + hiI) / 2; int midJ = (loJ + hiJ) / 2; if(matrix[midI][midJ] > target) { if(searchMatrix(matrix, target, loI, loJ, midI, midJ)) return true; // 1st quadrant if(searchMatrix(matrix, target, loI, midJ+1, midI, hiJ)) return true; // 2nd quadrant if(searchMatrix(matrix, target, midI+1, loJ, hiI, midJ)) return true; // 3rd quadrant } else if(matrix[midI][midJ] < target) { if(searchMatrix(matrix, target, loI, midJ+1, midI, hiJ)) return true; // 2nd quadrant if(searchMatrix(matrix, target, midI+1, loJ, hiI, midJ)) return true; // 3rd quadrant if(searchMatrix(matrix, target, midI+1, midJ+1, hiI, hiJ)) return true; // 4rd quadrant } else { return true; } return false; } };
-
-
方法2:二叉搜索树
-
思路:将矩阵视为二叉搜索树,根节点为矩阵右上角或左下角的节点。
-
时间:$O(m+n)$
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
class Solution { public: bool searchMatrix(vector<vector<int>>& matrix, int target) { if(matrix.empty()) return false; if(matrix[0].empty()) return false; int rows = matrix.size(); int cols = matrix[0].size(); int i = 0; int j = cols - 1; while(i < rows && j >= 0) { if(matrix[i][j] == target) return true; else if(matrix[i][j] > target) j--; else i++; } return false; } };
-
leetcode 4: 寻找两个有序数组的中位数
时间:$O(\log (n+m))$
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
def median(A, B):
m, n = len(A), len(B)
if m > n:
A, B, m, n = B, A, n, m
if n == 0:
raise ValueError
imin, imax, half_len = 0, m, (m + n + 1) / 2
while imin <= imax:
i = (imin + imax) / 2
j = half_len - i
if i < m and B[j-1] > A[i]:
# i is too small, must increase it
imin = i + 1
elif i > 0 and A[i-1] > B[j]:
# i is too big, must decrease it
imax = i - 1
else:
# i is perfect
if i == 0: max_of_left = B[j-1]
elif j == 0: max_of_left = A[i-1]
else: max_of_left = max(A[i-1], B[j-1])
if (m + n) % 2 == 1:
return max_of_left
if i == m: min_of_right = B[j]
elif j == n: min_of_right = A[i]
else: min_of_right = min(A[i], B[j])
return (max_of_left + min_of_right) / 2.0
leetcode 33: 搜索旋转排序数组
-
题意:旋转数组无重复
-
思路:分为左半边有序和右半边有序两种情况,左半边有序看target是否落入左半边,右半边有序看target是否落入右半边。
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
class Solution { public: int search(vector<int>& nums, int target) { int lo = 0; int hi = nums.size() - 1; while(lo <= hi) { int mid = (lo + hi) / 2; if(nums[mid] == target) return mid; // first half in order if(nums[lo] <= nums[mid]) { // nums[lo] <= target < nums[mid] if(nums[lo] <= target && target < nums[mid]) hi = mid - 1; else lo = mid + 1; // first half not in order } else { // nums[mid] < target <= nums[hi] if(nums[mid] < target && target <= nums[hi]) lo = mid + 1; else hi = mid - 1; } } return -1; } };
leetcode 81: 搜索旋转排序数组II
-
题意:旋转数组有重复
-
思路:与33题类似,但是需要额外考虑旋转点有重复,造成lo, mid, hi相等的情况。
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
class Solution { public: int search(vector<int>& nums, int target) { int lo = 0; int hi = nums.size() - 1; while(lo <= hi) { int mid = (lo + hi) / 2; if(nums[mid] == target) return true; // nums[lo] == nums[mid] == nums[hi] // [3 1 2 3 3 3 3] if(nums[lo] == nums[mid] && nums[mid] == nums[hi]) { lo++; hi--; // first half in order } else if(nums[lo] <= nums[mid]) { // nums[lo] <= target < nums[mid] if(nums[lo] <= target && target < nums[mid]) hi = mid - 1; else lo = mid + 1; // first half not in order } else { // nums[mid] < target <= nums[hi] if(nums[mid] < target && target <= nums[hi]) lo = mid + 1; else hi = mid - 1; } } return false; } };
leetcode 34: 在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
class Solution { public: vector<int> searchRange(vector<int>& nums, int target) { vector<int> notFound; notFound.push_back(-1); notFound.push_back(-1); if(nums.size() == 0) return notFound; int lo = binarySearch(nums, target); int hi = binarySearch(nums, target + 1); if(lo < nums.size() && nums[lo] == target) { vector<int> result; result.push_back(lo); result.push_back(hi - 1); return result; } return notFound; } private: int binarySearch(vector<int>& nums, int target) { int lo = 0; int hi = nums.size() - 1; while(lo <= hi) { int mid = (lo + hi) / 2; if(nums[mid] < target) lo = mid + 1; else hi = mid - 1; } return lo; } };
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42
class Solution { public: vector<int> searchRange(vector<int>& nums, int target) { vector<int> notFound; notFound.push_back(-1); notFound.push_back(-1); if(nums.size() == 0) return notFound; int lo = binarySearch(nums, target); int hi = binarySearchRight(nums, target); if(lo < nums.size() && nums[lo] == target) { vector<int> result; result.push_back(lo); result.push_back(hi - 1); return result; } return notFound; } private: int binarySearch(vector<int>& nums, int target) { int lo = 0; int hi = nums.size() - 1; while(lo <= hi) { int mid = (lo + hi) / 2; if(nums[mid] < target) lo = mid + 1; else hi = mid - 1; } return lo; } int binarySearchRight(vector<int>& nums, int target) { int lo = 0; int hi = nums.size() - 1; while(lo <= hi) { int mid = (lo + hi) / 2; if(nums[mid] <= target) lo = mid + 1; else hi = mid - 1; } return lo; } };
leetcode 35: 搜索插入位置
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
class Solution { public: int searchInsert(vector<int>& nums, int target) { int lo = 0; int hi = nums.size() - 1; while(lo <= hi) { int mid = (lo + hi) / 2; if (nums[mid] < target) lo = mid+1; else hi = mid-1; } return lo; } };
leetcode 540: 有序数组中的单一元素
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
class Solution { public int singleNonDuplicate(int[] nums) { int lo = 0; int hi = nums.length - 1; while(lo <= hi) { int mid = (lo + hi) / 2; if(mid >= 1 && nums[mid-1] == nums[mid]) { if((mid-2-lo+1) % 2 == 1) hi = mid - 2; else lo = mid + 1; } else if(mid < nums.length-1 && nums[mid+1] == nums[mid]) { if((mid-1-lo+1) % 2 == 1) hi = mid - 1; else lo = mid + 2; } else { return nums[mid]; } } return -1; } }
leetcode 162: 寻找峰值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
class Solution {
public:
int findPeakElement(vector<int>& nums) {
int lo = 0;
int hi = nums.size() - 1;
while(lo < hi) {
int mid1 = (lo + hi) / 2;
int mid2 = mid1 + 1;
if(nums[mid1] < nums[mid2]) lo = mid2;
else hi = mid1;
}
return lo;
}
};
散列
leetcode 1: 两数之和
-
题意:在数组中寻找两数之和等于目标值。
-
思路:用一个散列表记录数组中的值和索引的关系。
-
时间:$O(n)$
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
class Solution { public: vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) { vector<int> result(2); unordered_map<int, int> hash; for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) { if(hash.find(target - nums[i]) != hash.end()) { result[0] = hash[target - nums[i]]; result[1] = i; return result; } hash[nums[i]] = i; } return result; } };
leetcode 128: 最长连续序列
-
思路:对于每个数x,如果x-1不在集合里,就一直增长看最大能到多少。
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
class Solution { public: int longestConsecutive(vector<int>& nums) { unordered_set<int> set; for(int x: nums) { set.insert(x); } int res = 0; for(int x: nums) { if(!set.count(x-1)) { int y = x + 1; while(set.count(y)) { y++; } res = max(res, y-x); } } return res; } };
leetcode 217: 存在重复元素
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
class Solution {
public:
bool containsDuplicate(vector<int>& nums) {
unordered_set<int> set;
for(int num: nums) {
if(set.count(num)) return true;
set.insert(num);
}
return false;
}
};
leetcode 242: 有效的字母异位词
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
class Solution {
public:
bool isAnagram(string s, string t) {
if(s.length() != t.length()) return false;
unordered_map<char, int> map;
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
if(!map.count(s[i])) map[s[i]] = 0;
map[s[i]]++;
}
for(int i = 0; i < t.length(); i++) {
if(!map.count(t[i])) return false;
if(--map[t[i]] < 0) return false;
}
return true;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
class Solution {
public:
bool isAnagram(string s, string t) {
if(s.length() != t.length()) return false;
sort(s.begin(), s.end());
sort(t.begin(), t.end());
return s == t;
}
};
leetcode 347: 前 K 个高频元素
排序:$O(n \log n)$
先利用散列表统计次数,然后对值排序。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> topKFrequent(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
unordered_map<int, int> map;
for(int num: nums) {
if(!map.count(num)) map[num] = 0;
map[num]++;
}
vector<pair<int, int>> vec(map.begin(), map.end());
sort(vec.begin(), vec.end(), cmp);
vector<int> res;
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
res.push_back(vec[i].first);
}
return res;
}
private:
static bool cmp(const pair<int, int>& a, const pair<int, int>& b) {
return a.second > b.second;
}
};
桶排序:$O(n)$
先利用散列表统计次数,交换散列表的键和值,进行桶排序。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> topKFrequent(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
unordered_map<int, int> freq;
for(int num: nums) {
if(!freq.count(num)) freq[num] = 0;
freq[num]++;
}
unordered_map<int, vector<int>> bucket;
for(unordered_map<int, int>::iterator it = freq.begin(); it != freq.end(); it++) {
if(!bucket.count(it->second)) bucket[it->second] = vector<int>();
bucket[it->second].push_back(it->first);
// cout << it->second << ' ' << it->first << endl;
}
vector<int> res;
for(int i = nums.size(); i > 0 && res.size() < k; i--) {
if(bucket.count(i)) {
for(int num: bucket[i]) {
res.push_back(num);
if(res.size() == k) break;
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
leetcode 350: 两个数组的交集II
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> intersect(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
unordered_map<int, int> map;
for(int num: nums1) {
if(!map.count(num)) map[num] = 0;
map[num]++;
}
vector<int> res;
for(int num: nums2) {
if(map.count(num)) {
res.push_back(num);
if(--map[num] == 0) map.erase(num);
}
}
return res;
}
};
leetcode 380: 常数时间插入、删除和获取随机元素
散列+数组
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
class RandomizedSet {
public:
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
RandomizedSet() {
}
/** Inserts a value to the set. Returns true if the set did not already contain the specified element. */
bool insert(int val) {
if(map.count(val)) return false;
vec.push_back(val);
map[val] = vec.size() - 1;
return true;
}
/** Removes a value from the set. Returns true if the set contained the specified element. */
bool remove(int val) {
if(!map.count(val)) return false;
// notice case when val == last
int last = vec.back();
map[last] = map[val];
vec[map[val]] = last;
vec.pop_back();
map.erase(val);
return true;
}
/** Get a random element from the set. */
int getRandom() {
return vec[rand() % vec.size()];
}
private:
unordered_map<int, int> map;
vector<int> vec;
};
/**
* Your RandomizedSet object will be instantiated and called as such:
* RandomizedSet* obj = new RandomizedSet();
* bool param_1 = obj->insert(val);
* bool param_2 = obj->remove(val);
* int param_3 = obj->getRandom();
*/
974. 和可被 K 整除的子数组
思路:散列前缀数组mod K的结果。
数组
leetcode 41: 缺失的第一个正数
-
思路:扫描一遍尽量将每个数归位,然后再扫描一遍找出结果。
-
时间:$O(n)$
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
class Solution { public: int firstMissingPositive(vector<int>& nums) { int i = 1; while(i <= nums.size()) { // [1,1] while(nums[i-1] > 0 && nums[i-1] <= nums.size() && nums[i-1] != i && nums[i-1] != nums[nums[i-1]-1]) { swap(nums[i-1], nums[nums[i-1]-1]); } i++; } for(i = 1; i <= nums.size(); i++) { if(nums[i-1] != i) break; } return i; } };
leetcode 45: 跳跃游戏II
-
方法一:动态规划
-
时间$O(n^2)$,超时
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
class Solution { public: int jump(vector<int>& nums) { vector<int> dp(nums.size(), -1); dp[0] = 0; for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) { for(int j = i+1; j < nums.size() && j <= i+nums[i]; j++) { if(dp[i] != -1) { if(dp[j] == -1) dp[j] = dp[i] + 1; else dp[j] = min(dp[i] + 1, dp[j]); } } } return dp[nums.size()-1]; } };
-
-
方法2:greedy
-
时间:$O(n)$
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
class Solution { public: int jump(vector<int>& nums) { int jumps = 0; int curEnd = 0; int curFarthest = 0; for(int i = 0; i < nums.size()-1; i++) { curFarthest = max(curFarthest, i+nums[i]); if(i == curEnd) { curEnd = curFarthest; jumps++; } } return jumps; } };
-
leetcode 55: 跳跃游戏
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
class Solution { public: bool canJump(vector<int>& nums) { int reach = 0; int i = 0; for(; i < nums.size() && i <= reach; i++) { reach = max(reach, i+nums[i]); } return i == nums.size(); } };
leetcode 48: 旋转图像
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29
/* * clockwise rotate * first reverse up to down, then swap the symmetry * 1 2 3 7 8 9 7 4 1 * 4 5 6 => 4 5 6 => 8 5 2 * 7 8 9 1 2 3 9 6 3 */ void rotate(vector<vector<int> > &matrix) { reverse(matrix.begin(), matrix.end()); for (int i = 0; i < matrix.size(); ++i) { for (int j = i + 1; j < matrix[i].size(); ++j) swap(matrix[i][j], matrix[j][i]); } } /* * anticlockwise rotate * first reverse left to right, then swap the symmetry * 1 2 3 3 2 1 3 6 9 * 4 5 6 => 6 5 4 => 2 5 8 * 7 8 9 9 8 7 1 4 7 */ void anti_rotate(vector<vector<int> > &matrix) { for (auto vi : matrix) reverse(vi.begin(), vi.end()); for (int i = 0; i < matrix.size(); ++i) { for (int j = i + 1; j < matrix[i].size(); ++j) swap(matrix[i][j], matrix[j][i]); } }
leetcode 56: 合并分区
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> merge(vector<vector<int>>& intervals) { vector<vector<int>> res; if(intervals.empty()) return res; sort(intervals.begin(), intervals.end(), [](vector<int> a, vector<int> b){return a[0] < b[0];}); res.push_back(intervals[0]); for(int i = 1; i < intervals.size(); i++) { if(intervals[i][0] <= res.back()[1]) { res.back()[1] = max(intervals[i][1], res.back()[1]); } else { res.push_back(intervals[i]); } } return res; } };
leetcode 57: 插入区间
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> insert(vector<vector<int>>& intervals, vector<int>& newInterval) { vector<vector<int>> res; int i = 0; while(i < intervals.size() && intervals[i][1] < newInterval[0]) { res.push_back(intervals[i++]); } while(i < intervals.size() && intervals[i][0] <= newInterval[1]) { // newInterval = vector<int>{ // min(newInterval[0], intervals[i][0]), // max(newInterval[1], intervals[i][1])}; newInterval[0] = min(newInterval[0], intervals[i][0]); newInterval[1] = max(newInterval[1], intervals[i][1]); i++; } res.push_back(newInterval); while(i < intervals.size()) { res.push_back(intervals[i++]); } return res; } };
leetcode 73: 矩阵置零
-
思路:用第一行存每列是否有0,用第一列存每行是否有0,多用一个col0变量表示第0列是否有0.
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
class Solution { public: void setZeroes(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) { int rows = matrix.size(); int cols = matrix[0].size(); int col0 = 1; for(int i = 0; i < rows; i++) { if(matrix[i][0] == 0) col0 = 0; for(int j = 1; j < cols; j++) { if(matrix[i][j] == 0) { matrix[i][0] = 0; matrix[0][j] = 0; } } } for(int i = rows - 1; i >= 0; i--) { for(int j = cols - 1; j >= 1; j--) { if(matrix[i][0] == 0 || matrix[0][j] == 0) { matrix[i][j] = 0; } } if(col0 == 0) matrix[i][0] = 0; } } };
leetcode 89: 格雷编码
-
思路:规律是第一位改变,后面的位倒序
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
class Solution { public: vector<int> grayCode(int n) { vector<int> res; res.push_back(0); for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) { int size = res.size(); for(int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--) { res.push_back(res[i] | 1<<j); } } return res; } };
leetcode 134: 加油站
思路:如果加油间耗油小于0,则重当前点重新开始。如果总加油减耗油小于0,则不能开车一圈。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
class Solution {
public:
int canCompleteCircuit(vector<int>& gas, vector<int>& cost) {
int start = 0;
int total = 0;
int tank = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < gas.size(); i++) {
tank += gas[i] - cost[i];
total += gas[i] - cost[i];
if(tank < 0) {
start = i + 1;
tank = 0;
}
}
return total<0? -1:start;
}
};
leetcode 136: 只出现一次的数字
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
class Solution {
public:
int singleNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
res ^= nums[i];
}
return res;
}
};
leetcode 137: 只出现一次的数字II
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
/*
n a b a b
1 0 0 0 1
1 0 1 1 0
1 1 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 1
0 1 0 1 0
a = a'bn + ab'n'
b = a'b'n + a'bn'
*/
class Solution {
public:
int singleNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
int a_last = a;
int b_last = b;
a = (~a_last & b_last & nums[i]) | (a_last & ~b_last & ~nums[i]);
b = (~a_last & ~b_last & nums[i]) | (~a_last & b_last & ~nums[i]);
}
return b;
}
};
剑指 Offer 56 - I. 数组中数字出现的次数
思路:先对所有数字进行一次异或,得到两个出现一次的数字的异或值。在异或结果中找到任意为 1 的位。根据这一位对所有的数字进行分组。在每个组内进行异或操作,得到两个数字。
leetcode 169: 多数元素
方法1:散列表
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
class Solution {
public:
int majorityElement(vector<int>& nums) {
unordered_map<int, int> map;
int n = nums.size();
for(int num: nums) {
if(!map.count(num)) map[num] = 0;
map[num]++;
if(map[num] > n/2) return num;
}
return 0;
}
};
方法2:Boyer-Moore Majority Vote Algorithm
不一样的数互相抵消,最后剩下没抵消的就是结果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
class Solution {
public:
int majorityElement(vector<int>& nums) {
int major = nums[0];
int count = 1;
int n = nums.size();
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if(count == 0) {
major = nums[i];
count++;
} else if(major == nums[i]) {
count++;
} else {
count--;
}
}
return major;
}
};
leetcode 189: 旋转数组
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
class Solution {
public:
void rotate(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
k = k % nums.size();
reverse(nums.begin(), nums.end());
reverse(nums.begin(), nums.begin()+k);
reverse(nums.begin()+k, nums.end());
}
};
leetcode 268: 缺失数字
方法1:xor
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
class Solution {
public:
int missingNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
int res = nums.size();
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
res ^= i ^ nums[i];
}
return res;
}
};
方法2:求和
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
class Solution {
public:
int missingNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
long sum = nums.size();
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
sum += i - nums[i];
}
return sum;
}
};
leetcode 287: 寻找重复数
剑指offer上的方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
class Solution {
public int findDuplicate(int[] nums) {
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
while(nums[i]-1 != i) {
if(nums[i] == nums[nums[i]-1]) return nums[i];
swap(nums, i, nums[i]-1);
}
}
return -1;
}
private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
int tmp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = tmp;
}
}
cycle detection
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
class Solution {
public:
int findDuplicate(vector<int>& nums) {
int slow = 0;
int fast = 0;
do {
slow = nums[slow];
fast = nums[nums[fast]];
} while(slow != fast);
int ptr1 = 0;
int ptr2 = slow;
while(ptr1 != ptr2) {
ptr1 = nums[ptr1];
ptr2 = nums[ptr2];
}
return ptr1;
}
};
leetcode 384: 打乱数组
Fisher-Yates Algorithm
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
class Solution {
public:
Solution(vector<int>& nums) {
original = nums;
}
/** Resets the array to its original configuration and return it. */
vector<int> reset() {
return original;
}
/** Returns a random shuffling of the array. */
vector<int> shuffle() {
vector<int> shuffle(original);
for(int i = 0; i < shuffle.size(); i++) {
swap(shuffle[i], shuffle[rand()%shuffle.size()]);
}
return shuffle;
}
private:
vector<int> original;
};
leetcode 324: 摆动排序
方法1:时间$O(n\log n)$,空间$O(n)$
小的一半(可能多一个)放偶数位,大的一半放奇数位,翻转是为了避免[4,5,5,6] => [5,6,4,5]这种情况。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
class Solution {
public:
void wiggleSort(vector<int>& nums) {
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
int half = nums.size()%2==0? nums.size()/2: nums.size()/2+1;
vector<int> small(nums.begin(), nums.begin()+half);
reverse(small.begin(), small.end());
vector<int> large(nums.begin()+half, nums.end());
reverse(large.begin(), large.end());
for(int i = 0; i < small.size(); i++) {
nums[2*i] = small[i];
}
for(int i = 0; i < large.size(); i++) {
nums[2*i+1] = large[i];
}
}
};
方法2:时间$O(n)$
leetcode 75 颜色分类 + leetcode 215 快速选择
先用$O(n)$快速选择出中位数,再用$O(n)$,大于中位数的到左边(映射到奇数位),小于中位数的到右边(映射到偶数位)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Accessing A(0) actually accesses nums[1].
Accessing A(1) actually accesses nums[3].
Accessing A(2) actually accesses nums[5].
Accessing A(3) actually accesses nums[7].
Accessing A(4) actually accesses nums[9].
Accessing A(5) actually accesses nums[0].
Accessing A(6) actually accesses nums[2].
Accessing A(7) actually accesses nums[4].
Accessing A(8) actually accesses nums[6].
Accessing A(9) actually accesses nums[8].
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
class Solution {
public:
void wiggleSort(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
auto midptr = nums.begin() + n/2;
nth_element(nums.begin(), midptr, nums.end());
int mid = *midptr;
#define A(i) nums[(1+2*(i)) % (n|1)]
int left = 0;
int right = n - 1;
int i = 0;
while(i <= right) {
if(A(i) > mid) swap(A(i++), A(left++));
else if(A(i) < mid) swap(A(i), A(right--));
else i++;
}
}
};
剑指 Offer 51. 数组中的逆序对
思路:归并排序,归并的时候,右半边数与左半边剩下的数构成逆序关系
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
public class Solution {
public int reversePairs(int[] nums) {
int len = nums.length;
if (len < 2) {
return 0;
}
int[] copy = new int[len];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
copy[i] = nums[i];
}
int[] temp = new int[len];
return reversePairs(copy, 0, len - 1, temp);
}
/**
* nums[left..right] 计算逆序对个数并且排序
*/
private int reversePairs(int[] nums, int left, int right, int[] temp) {
if (left == right) {
return 0;
}
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
int leftPairs = reversePairs(nums, left, mid, temp);
int rightPairs = reversePairs(nums, mid + 1, right, temp);
if (nums[mid] <= nums[mid + 1]) {
return leftPairs + rightPairs;
}
int crossPairs = mergeAndCount(nums, left, mid, right, temp);
return leftPairs + rightPairs + crossPairs;
}
/**
* nums[left..mid] 有序,nums[mid + 1..right] 有序
*/
private int mergeAndCount(int[] nums, int left, int mid, int right, int[] temp) {
for (int i = left; i <= right; i++) {
temp[i] = nums[i];
}
int i = left;
int j = mid + 1;
int count = 0;
for (int k = left; k <= right; k++) {
if (i == mid + 1) {
nums[k] = temp[j];
j++;
} else if (j == right + 1) {
nums[k] = temp[i];
i++;
} else if (temp[i] <= temp[j]) {
nums[k] = temp[i];
i++;
} else {
nums[k] = temp[j];
j++;
count += (mid - i + 1);
}
}
return count;
}
}
字符串
leetcode 5: 最长回文子串
-
方法1:中心扩展
-
时间:$O(n^2)$,空间:$O(1)$
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
class Solution { public: string longestPalindrome(string s) { if(s == "") return s; string longest = s.substr(0, 1); for(int i = 0; i < s.length() - 1; i++) { string s1 = expandAroundCenter(s, i, i); if(s1.length() > longest.length()) longest = s1; string s2 = expandAroundCenter(s, i, i + 1); if(s2.length() > longest.length()) longest = s2; } return longest; } string expandAroundCenter(string s, int l, int r) { while(l >= 0 && r < s.length() && s[l] == s[r]) { l--; r++; } l++; r--; return s.substr(l, r - l + 1); } };
-
-
方法2:动态规划
-
思路:二维数组存起点到终点是否回文
-
时间$O(n^2)$,空间$O(n^2)$
-
leetcode 10: 正则表达式匹配
-
题意:’.’ 匹配任意单个字符,’*’ 匹配零个或多个前面的那一个元素
-
方法1:动态规划
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36
class Solution { public: bool isMatch(string s, string p) { int m = s.length(); int n = p.length(); bool dp[m+1][n+1]; dp[0][0] = true; for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { dp[i][0] = false; } for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++) { if(p[j-1] == '*' && j-2 >= 0 && dp[0][j-2] == true) dp[0][j] = true; else dp[0][j] = false; } for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++) { if(s[i-1] == p[j-1] || p[j-1] == '.') dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1]; else if(p[j-1] == '*') { if(s[i-1] == p[j-2] || p[j-2] == '.') dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] // in this case, a* counts as multiple a // || dp[i][j-1] // in this case, a* counts as single a || dp[i][j-2]; // in this case, a* counts as empty else dp[i][j] = dp[i][j-2]; // in this case, a* only counts as empty } else dp[i][j] = false; } } for(int i = 0; i <= m; i++) { for(int j = 0; j <= n; j++) { cout << dp[i][j] << ' '; } cout << endl; } return dp[m][n]; } };
-
-
方法2:递归(不太容易理解)
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
class Solution { public: bool isMatch(string s, string p) { return isMatch(s, p, 0, 0); } private: bool isMatch(string& s, string& p, int cur1, int cur2) { if(cur1 == s.length() && cur2 == p.length()) return true; if(cur1 > s.length() || cur2 > p.length()) return false; if(cur2+1 < p.length() && p[cur2+1] == '*') { if(isMatch(s, p, cur1, cur2+2)) return true; if(cur1 != s.length() && cur2 != p.length() && (s[cur1] == p[cur2] || p[cur2] == '.') && isMatch(s, p, cur1+1, cur2)) return true; } else { if(cur1 != s.length() && cur2 != p.length() && (s[cur1] == p[cur2] || p[cur2] == '.') && isMatch(s, p, cur1+1, cur2+1)) return true; } return false; } };
-
leetcode 44: 通配符匹配
-
题意:’?’ 可以匹配任何单个字符,’*’ 可以匹配任意字符串(包括空字符串)。
-
方法1:迭代
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23
class Solution { public: bool isMatch(string s, string p) { int cur1 = 0; int cur2 = 0; int match; int star = -1; while(cur1 < s.length()) { if(cur2 < p.length() && (s[cur1] == p[cur2] || p[cur2] == '?')) { cur1++; cur2++; } else if(cur2 < p.length() && p[cur2] == '*') { match = cur1; star = cur2++; } else if(star >= 0) { cur1 = ++match; cur2 = star + 1; } else return false; } while(cur2 < p.length() && p[cur2] == '*') cur2++; return cur2 == p.length(); } };
-
方法2:递归(不太容易理解)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23
class Solution { public: bool isMatch(string s, string p) { int numStar = 0; return isMatch(s, p, 0, 0, numStar); } private: bool isMatch(string s, string p, int cur1, int cur2, int& numStar) { if(cur1 == s.length() && cur2 == p.length()) return true; int curNumStar = numStar; if(s[cur1] == p[cur2] || p[cur2] == '?') { if(isMatch(s, p, cur1+1, cur2+1, numStar)) return true; } else if(p[cur2] == '*') { for(int i = 0; cur1+i <= s.length(); i++) { if(i == 0) numStar++; if(isMatch(s, p, cur1+i, cur2+1, numStar)) return true; if(numStar > curNumStar+1) return false; } } return false; } };
-
方法3:动态规划
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
class Solution { public: bool isMatch(string s, string p) { int m = s.length(); int n = p.length(); bool dp[m+1][n+1]; dp[0][0] = true; for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { dp[i][0] = false; } for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++) { dp[0][j] = false; } for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++) { if(p[j-1] == '*') dp[0][j] = true; else break; } for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++) { // if(p[j-1] != '*') dp[i][j] == dp[i-1][j-1] && (s[i-1] == p[j-1] || p[j-1] == '?'); // else dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] || dp[i][j-1]; if(s[i-1] == p[j-1] || p[j-1] == '?') dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1]; // p[j-1] == '*', s[i-1], p[j-1] else if(p[j-1] == '*') dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] || dp[i][j-1]; else dp[i][j] = false; } } return dp[m][n]; } };
leetcode 28: 子字符串查找
-
时间:最坏情况$O(NM)$,但是实际运行时间一般为$O(N+M)$,KMP为$O(N+M)$
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
class Solution { public: int strStr(string haystack, string needle) { if(needle == "") return 0; int N = haystack.length(); int M = needle.length(); for(int i = 0; i <= N - M; i++) { int j; for(j = 0; j < M; j++) if(haystack[i+j] != needle[j]) break; if(j == M) return i; } return -1; } };
leetcode 97: 交错字符串
-
方法1:带缓存的dfs
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22
class Solution { public: bool isInterleave(string s1, string s2, string s3) { if(s3.length() != s1.length() + s2.length()) return false; vector<vector<bool>> valid = vector<vector<bool>>(s1.length()+1, vector<bool>(s2.length()+1, true)); return isInterleave(s1, s2, s3, 0, 0, 0, valid); } private: bool isInterleave(string& s1, string& s2, string& s3, int cur1, int cur2, int cur3, vector<vector<bool>>& valid) { if(cur3 == s3.length()) return true; if(valid[cur1][cur2] == false) return false; if(cur1 < s1.length() && s3[cur3] == s1[cur1]) { if(isInterleave(s1, s2, s3, cur1+1, cur2, cur3+1, valid)) return true; } if(cur2 < s2.length() && s3[cur3] == s2[cur2]) { if(isInterleave(s1, s2, s3, cur1, cur2+1, cur3+1, valid)) return true; } valid[cur1][cur2] = false; return false; } };
-
方法2:动态规划
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
class Solution { public: bool isInterleave(string s1, string s2, string s3) { if(s1.length() + s2.length() != s3.length()) return false; bool dp[s1.length()+1][s2.length()+1]; for(int i = 0; i < s1.length()+1; i++) { for(int j = 0; j < s2.length()+1; j++) { if(i==0 && j==0) dp[i][j] = true; else if(i == 0) dp[i][j] = (dp[i][j-1] && s2[j-1] == s3[i+j-1]); else if(j == 0) dp[i][j] = (dp[i-1][j] && s1[i-1] == s3[i+j-1]); else dp[i][j] = (dp[i-1][j] && s1[i-1] == s3[i+j-1] ) || (dp[i][j-1] && s2[j-1] == s3[i+j-1] ); } } return dp[s1.length()][s2.length()]; } };
-
方法3:bfs(不推荐)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38
class Solution { public: bool isInterleave(string s1, string s2, string s3) { if(s1.length() + s2.length() != s3.length()) return false; bool marked[s1.length()+1][s2.length()+1]; for(int i = 0; i < s1.length()+1; i++) { for(int j = 0; j < s2.length()+1; j++) { marked[i][j] = false; } } queue<vector<int>> q; marked[0][0] = true; q.push(vector<int>{0, 0}); while(!q.empty()) { vector<int> v = q.front(); q.pop(); int x = v[0]; int y = v[1]; if(x == s1.length() && y == s2.length()) return true; // return here if(s3[x+y] == s1[x]) { if(x+1 < s1.length()+1 && marked[x+1][y] == false) { marked[x+1][y] = true; q.push(vector<int>{x+1, y}); // if(x+1 == s1.length() && y == s2.length()) return true; } } if(s3[x+y] == s2[y]) { if(y+1 < s2.length()+1 && marked[x][y+1] == false) { marked[x][y+1] = true; q.push(vector<int>{x, y+1}); // if(x == s1.length() && y+1 == s2.length()) return true; } } } return false; } };
leetcode 131: 分割回文数
-
方法1:回溯法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36
class Solution { public: vector<vector<string>> partition(string s) { vector<vector<string>> res; vector<string> cur; backtrack(s, 0, cur, res); return res; } private: void backtrack(string s, int start, vector<string>& cur, vector<vector<string>>& res) { if(start == s.length()) { res.push_back(cur); return; } for(int i = start+1; i <= s.length(); i++) { if(isPalindrome(s, start, i)) { string word = s.substr(start, i-start); cur.push_back(word); backtrack(s, i, cur, res); cur.pop_back(); } } } bool isPalindrome(string& s, int start, int end) { end--; while(start < end) { if(s[start] != s[end]) return false; start++; end--; } return true; } };
-
方法2:带缓存的dfs
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34
class Solution { public: vector<vector<string>> partition(string s) { if(map.count(s)) return map[s]; if(s.length() == 0) return vector(1, vector<string>()); vector<vector<string>> res; for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) { string word = s.substr(i); if(isPalindrome(word)) { string left = s.substr(0, i); vector<vector<string>> leftPatition = partition(left); for(vector<string> vec: leftPatition) { vec.push_back(word); res.push_back(vec); } } } map[s] = res; return res; } private: bool isPalindrome(string s) { for(int i = 0; i < s.length()/2; i++) { if(s[i] != s[s.length()-i-1]) { return false; } } return true; } unordered_map<string, vector<vector<string>>> map; };
-
方法3:动态规划
思路:第一重循环记录字符串每个索引位置的结果,第二重循环遍历每个结果。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32
class Solution { public: vector<vector<string>> partition(string s) { unordered_map<int, vector<vector<string>>> dp; dp[0] = vector(1, vector<string>()); for(int i = 1; i <= s.length(); i++) { vector<vector<string>> res; for(int j = 0; j < i; j++) { if(dp.count(j) && isPalindrome(s, j, i)) { vector<vector<string>> memo = dp[j]; for(vector<string> vec: memo) { vec.push_back(s.substr(j, i-j)); res.push_back(vec); } } } if(!res.empty()) dp[i] = res; } return dp.count(s.length())? dp[s.length()]: vector<vector<string>>(); } private: bool isPalindrome(string& s, int start, int end) { end--; while(start < end) { if(s[start] != s[end]) return false; start++; end--; } return true; } };
leetcode 132: 分割回文串II
思路:长度为n的字符串最多需要n-1次分割。i为中心,j为半径,分回文串长度为奇偶两种情况。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
class Solution {
public:
int minCut(string s) {
vector<int> dp(s.length()+1, 0);
for(int i = 0; i < s.length()+1; i++) {
dp[i] = i-1;
}
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
for(int j = 0; i-j >= 0 && i+j < s.length() && s[i-j] == s[i+j]; j++) {
dp[i+j+1] = min(dp[i+j+1], dp[i-j]+1);
}
for(int j = 0; i-j+1 >= 0 && i+j < s.length() && s[i-j+1] == s[i+j]; j++) {
dp[i+j+1] = min(dp[i+j+1], dp[i-j+1]+1);
}
}
return dp[s.length()];
}
};
leetcode 139: 单词拆分
-
方法1:回溯法(超时)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
class Solution { public: bool wordBreak(string s, vector<string>& wordDict) { return backtrack(0, s, wordDict); } private: bool backtrack(int cur, string& s, vector<string>& wordDict) { if(cur == s.length()) return true; for(string word: wordDict) { if(s.substr(cur, word.length()) == word) { if(backtrack(cur+word.length(), s, wordDict)) return true; } } return false; } };
-
方法2:动态规划
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
// DP (better) // O(m*n) m=s.length() n=wordDict.length() class Solution { public: bool wordBreak(string s, vector<string>& wordDict) { vector<bool> dp(s.length()+1, false); dp[0] = true; for(int i = 1; i <= s.length(); i++) { for(string word: wordDict) { // i-word.length() overflow int j = i - word.length(); if(j >= 0 && dp[j] && s.substr(j, word.length()) == word) { dp[i] = true; } } } return dp[s.length()]; } };
-
方法3:动态规划
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23
// DP // O(m^2) m=s.length() n=wordDict.length() class Solution { public: bool wordBreak(string s, vector<string>& wordDict) { unordered_set<string> dict; for(string word: wordDict) { dict.insert(word); } vector<bool> dp(s.length()+1, false); dp[0] = true; for(int i = 1; i <= s.length(); i++) { for(int j = i-1; j >= 0; j--) { if(dp[j] && dict.find(s.substr(j, i-j)) != dict.end()) { dp[i] = true; break; } } } return dp[s.length()]; } };
leetcode 140: 单词拆分II
-
方法1:回溯法(超时)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22
class Solution { public: vector<string> wordBreak(string s, vector<string>& wordDict) { vector<string> results; backtrack(0, s, wordDict, "", results); return results; } private: void backtrack(int cur, string& s, vector<string>& wordDict, string res, vector<string>& results) { if(cur == s.length()) { results.push_back(res); return; } for(string word: wordDict) { if(s.substr(cur, word.length()) == word) { backtrack(cur+word.length(), s, wordDict, res.empty()? word:res+' '+word, results); } } } };
-
方法2:带缓存的dfs
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35
class Solution { public: vector<string> wordBreak(string s, vector<string>& wordDict) { unordered_set<string> dict; for(string word: wordDict) { dict.insert(word); } unordered_map<string, vector<string>> map; return dfs(s, dict, map); } private: vector<string> dfs(string s, unordered_set<string>& dict, unordered_map<string, vector<string>>& map) { if(map.find(s) != map.end()) return map[s]; vector<string> res; if(s.empty()) { res.push_back(""); return res; } for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) { string word = s.substr(i); if(dict.find(word) != dict.end()) { string left = s.substr(0, i); vector<string> v = dfs(left, dict, map); for(string str: v) { res.push_back(str.empty()? word: str+" "+word); } } } map[s] = res; return res; } };
-
动态规划(超时)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23
class Solution { public: vector<string> wordBreak(string s, vector<string>& wordDict) { unordered_map<int, vector<string>> map; map[0] = vector<string>{ "" }; for(int i = 1; i <= s.length(); i++) { vector<string> res; for(string word: wordDict) { int j = i - word.length(); if(j >= 0 && map.find(j) != map.end() && s.substr(j, word.length()) == word) { vector<string> mem = map[j]; for(string str: mem) { res.push_back(str.empty()? word: str+' '+word); } } } if(!res.empty()) map[i] = res; } return (map.find(s.length())==map.end())? vector<string>(): map[s.length()]; } };
leetcode 395: 至少有K个重复字符的最长子串
双指针
leetcode 3: 无重复字符的最长子字符串
-
思路:双指针。
利用散列表记录所有当前字符串中字符出现的位置。尽可能将右指针向右移动,直到出现重复的字符,这时将左指针向右移去除重复的字符。
-
时间:$O(n)$
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
class Solution { public: int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) { unprdered_map<char, int> m; int start = 0; int max = 0; for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) { char c = s[i]; if(m.find(c) != m.end()) start = std::max(start, m[c] + 1); max = std::max(max, i - start + 1); m[c] = i; } return max; } };
leetcode 11: 盛最多水的容器
-
思路:双指针
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
class Solution { public: int maxArea(vector<int>& height) { int max = 0; int l =0; int r = height.size() - 1; while(l < r) { int area = (r - l) * std::min(height[l], height[r]); max = std::max(max, area); if(height[l] < height[r]) l++; else r--; } return max; } };
leetcode 15: 三数之和
-
思路:双指针
首先排序,然后对于每一个数,利用双指针找到另两个数。
-
时间:$O(n^2)$,空间:$O(1)$(如果用散列表记录需要$O(n)$)
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> threeSum(vector<int>& nums) { std::sort(nums.begin(), nums.end()); vector<vector<int>> result; if(nums.size() < 3) return result; for(int i = 0; i < nums.size() - 2; i++) { if(i != 0 && nums[i] == nums[i-1]) continue; int left = i + 1; int right = nums.size() - 1; int sum = - nums[i]; while(left < right) { if(nums[left] + nums[right] == sum) { vector<int> v = { nums[i], nums[left], nums[right] }; result.push_back(v); while(left < right && nums[left] == nums[left + 1]) left++; while(left < right && nums[right] == nums[right - 1]) right--; left++; right--; } else if (nums[left] + nums[right] > sum) { right--; } else { //nums[left] + nums[right] < sum left++; } } } return result; } };
leetcode 16: 最接近的三数之和
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26
class Solution { public: int threeSumClosest(vector<int>& nums, int target) { int closest = 0; if(nums.size() < 3) return closest; std::sort(nums.begin(), nums.end()); closest = nums[0] + nums[1] + nums[2]; for(int i = 0; i < nums.size() - 2; i++) { int left = i + 1; int right = nums.size() - 1; while(left < right) { int sum = nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right]; if(target == sum) { return target; } else if(target > sum) { if(std::abs(target - closest) > std::abs(target - sum)) closest = sum; left++; } else { //target < sum if(std::abs(target - closest) > std::abs(target - sum)) closest = sum; right--; } } } return closest; } };
leetcode 18: 四数之和
-
时间:$O(n^3)$,空间:$O(1)$(如果用散列表记录需要$O(n)$)
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> fourSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) { vector<vector<int>> result; if(nums.size() < 4) return result; std::sort(nums.begin(), nums.end()); for(int i = 0; i < nums.size() - 3; i++) { if(i != 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) continue; for(int j = i + 1; j < nums.size() - 2; j++) { if(j != i + 1 && nums[j] == nums[j - 1]) continue; int left = j + 1; int right = nums.size() - 1; int sum = target - nums[i] - nums[j]; while(left < right) { if(sum == nums[left] + nums[right]) { vector<int> v = { nums[i], nums[j], nums[left], nums[right] }; result.push_back(v); while(left < right && nums[left] == nums[left + 1]) left++; while(left < right && nums[right] == nums[right - 1]) right--; left++; right--; } else if(sum > nums[left] + nums[right]) { left++; } else { //sum < nums[left] + nums[right] right--; } } } } return result; } };
leetcode 26: 删除排序数组中的重复项
-
思路:双指针。
-
时间:$O(n)$
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
class Solution { public: int removeDuplicates(vector<int>& nums) { int count = 0; int n = nums.size(); for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){ if(nums[i] == nums[i-1]) count++; else nums[i-count] = nums[i]; } return n-count; } };
leetcode 27: 移除元素
- 思路:跟26题类似,双指针。
leetcode 30: 串联所有单词的子串
leetcode 42: 接雨水
-
思路:双指针
-
时间:$O(n)$
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22
class Solution { public: int trap(vector<int>& height) { int left = 0; int right = height.size() - 1; int maxLeft = 0; int maxRight = 0; int res = 0; while(left <= right) { if(maxLeft <= maxRight) { if(height[left] > maxLeft) maxLeft = height[left]; else res += maxLeft - height[left]; left++; } else { if(height[right] > maxRight) maxRight = height[right]; else res += maxRight - height[right]; right--; } } return res; } };
leetcode 75: 颜色分类
-
思路:双指针
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29
class Solution { public: void sortColors(vector<int>& nums) { int left = 0; int right = nums.size() - 1; // for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) { for(int i = 0; i <= right; i++) { // swapping following 2 lines causes errors // [1,2,0] => [1,0,2] while(nums[i] == 2 && i < right) swap(nums[i], nums[right--]); while(nums[i] == 0 && i > left) swap(nums[i], nums[left++]); } } }; // another solution, more clear class Solution { public: void sortColors(vector<int>& nums) { int left = 0; int right = nums.size() - 1; for(int i = 0; i <= right; i++) { // there is no need of mutiple oprations here // because nums[left] == 1 unless i == left if (nums[i] == 0) swap(nums[i], nums[left++]); else if (nums[i] == 2) swap(nums[i--], nums[right--]); } } };
leetcode 76: 最小覆盖子串
-
思路
双指针,左右指针归零,右指针往右找到一个可行解,左指针往右减少长度直到不可行。
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
class Solution { public: string minWindow(string s, string t) { vector<int> map(128, 0); for(auto c: t) map[c]++; int counter = t.length(); int begin = 0, end = 0; int dist = INT_MAX; int head = 0; while(end < s.length()) { if(map[s[end++]]-- > 0) counter--; while(counter == 0) { if(end - begin < dist) dist = end - (head = begin); if(map[s[begin++]]++ == 0) counter++; } } return dist == INT_MAX ? "" : s.substr(head, dist); } };
leetcode 80: 删除排序数组中的重复项II
-
思路:双指针
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
class Solution { public: int removeDuplicates(vector<int>& nums) { if(nums.size() == 0) return 0; int idx = 1; int cnt = 1; int lastNum = nums[0]; for(int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i++) { if(nums[i] == lastNum) { if(++cnt <= 2) nums[idx++] = nums[i]; } else { cnt = 1; lastNum = nums[i]; nums[idx++] = nums[i]; } } return idx; } };
leetcode 283: 移动零
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
class Solution {
public:
void moveZeroes(vector<int>& nums) {
int count = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
if(nums[i] != 0) {
nums[count++] = nums[i];
}
}
for(; count < nums.size(); count++) {
nums[count] = 0;
}
}
};
剑指 Offer 57. 和为s的两个数字
思路:双指针
剑指 Offer 57 - II. 和为s的连续正数序列
思路:双指针
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer> > FindContinuousSequence(int sum) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
int start = 1;
int end = 1;
int curSum = 1;
while (start <= sum) {
if (curSum == sum) {
if (end > start) {
ArrayList<Integer> sequence = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) {
sequence.add(i);
}
res.add(sequence);
}
curSum -= start++;
} else if (curSum > sum) {
curSum -= start++;
} else {
curSum += ++end;
}
}
return res;
}
}
栈
leetcode 20: 有效的括号
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
class Solution { public: bool isValid(string s) { stack<int> st; int length = s.length(); for(int i = 0; i < length; i++) { switch(s[i]) { case'(': st.push(0); break; case')': if(st.empty() || st.top() != 0) return false; st.pop(); break; case'{': st.push(1); break; case'}': if(st.empty() || st.top() != 1) return false; st.pop(); break; case'[': st.push(2); break; case']': if(st.empty() || st.top() != 2) return false; st.pop(); break; } } if(!st.empty()) return false; return true; } };
leetcode 32: 最长有效括号
-
方法1:暴力
-
时间:$O(n^2)$
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
class Solution { public: int longestValidParentheses(string s) { if(s == "") return 0; int res = 0; for(int i = 0; i < s.length()-1; i++) { int parentheses = 0; for(int j = i; j < s.length(); j++) { if(s[j] == '(') parentheses++; else parentheses--; if(parentheses < 0) break; else if(parentheses == 0) res = max(res, j-i+1); } } return res; } };
-
-
方法2:栈
-
思路:如果遇到右括号匹配错误,将右括号索引入栈,最后出栈时计算两次匹配错误间的长度。
-
时间:$O(n)$
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
class Solution { public: int longestValidParentheses(string s) { stack<int> st; for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) { if(s[i] == '(') st.push(i); else if(!st.empty() && s[st.top()] == '(') st.pop(); else st.push(i); } int res = 0; int last = s.length(); while(!st.empty()) { res = max(res, last-st.top()-1); last = st.top(); st.pop(); } res = max(res, last); return res; } };
-
leetcode 84: 柱状图中最大矩形
-
方法1:分治
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39
// devide and conquer // two pointers // O(nlogn) // T(n) = 2T(n/2) + O(n) class Solution { public: int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights) { if(heights.empty()) return 0; return largestRectangleArea(heights, 0, heights.size() - 1); } private: int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights, int lo, int hi) { if(lo == hi) return heights[lo]; int mid = (lo + hi) / 2; // left part, right part or combine 2 parts int area = largestRectangleArea(heights, lo, mid); area = max(area, largestRectangleArea(heights, mid+1, hi)); area = max(area, largestCombineArea(heights, lo, mid, hi)); return area; } int largestCombineArea(vector<int>& heights, int lo, int mid, int hi) { int left = mid; int right = mid + 1; int area = 0; int h = INT_MAX; while(left >= lo && right <= hi) { h = min(h, min(heights[left], heights[right])); area = max(area, h * (right - left + 1)); if(left == lo) right++; else if(right == hi) left--; else if(heights[left-1] > heights[right+1]) left--; else right++; } return area; } };
-
方法2
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
class Solution { public: int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights) { if(heights.empty()) return 0; vector<int> lessFromLeft(heights.size(), -1); for(int i = 1; i < heights.size(); i++) { int p = i - 1; while(p >= 0 && heights[p] >= heights[i]) { p = lessFromLeft[p]; } lessFromLeft[i] = p; } vector<int> lessFromRight(heights.size(), heights.size()); for(int i = heights.size() - 2; i >= 0; i--) { int p = i + 1; while(p < heights.size() && heights[p] >= heights[i]) { p = lessFromRight[p]; } lessFromRight[i] = p; } int maxArea = 0; for(int i = 0; i < heights.size(); i++) { // cout << heights[i] << " " << (lessFromRight[i]-lessFromLeft[i]-1) << endl; maxArea = max(maxArea, heights[i] * (lessFromRight[i]-lessFromLeft[i]-1)); } return maxArea; } };
-
方法3:栈
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22
// stack O(n) // 2 1 5 6 2 3 class Solution { public: int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights) { if(heights.empty()) return 0; int res = 0; heights.push_back(0); stack<int> s; for(int i = 0; i < heights.size(); i++) { while(!s.empty() && heights[i] < heights[s.top()]) { int h = heights[s.top()]; s.pop(); int w = s.empty()? i: i - s.top() - 1; // (i - 1) - (s.top + 1) + 1 res = max(res, h * w); } s.push(i); } return res; } };
leetcode 150: 逆波兰表达式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
class Solution {
public:
int evalRPN(vector<string>& tokens) {
stack<int> st;
for(int i = 0; i < tokens.size(); i++) {
string s = tokens[i];
if(isdigit(s[0])) {
st.push(stoi(s));
} else if(s.size() > 1 && s[0] == '-') {
st.push(-stoi(s.substr(1)));
} else {
int operand2 = st.top();
st.pop();
int operand1 = st.top();
st.pop();
switch(s[0]) {
case '+':
st.push(operand1 + operand2);
break;
case '-':
st.push(operand1 - operand2);
break;
case '*':
st.push(operand1 * operand2);
break;
case '/':
st.push(operand1 / operand2);
break;
}
}
}
return st.top();
}
};
leetcode 227: 基本计算器II
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
class Solution {
public:
int calculate(string s) {
stringstream ss('+'+s);
char oprt;
int opnd;
int res = 0;
int last = 0;
while(ss >> oprt >> opnd) {
if(oprt == '+' || oprt == '-') {
res += last;
last = 0;
last += oprt=='+'? opnd: -opnd;
} else {
last = oprt=='*'? last*opnd: last/opnd;
}
}
res += last;
return res;
}
};
leetcode 155: 最小栈
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
class MinStack {
public:
/** initialize your data structure here. */
MinStack() {
}
void push(int x) {
if(minNumStack.empty() || x <= minNumStack.top()) minNumStack.push(x);
numStack.push(x);
}
void pop() {
if(numStack.top() == minNumStack.top()) minNumStack.pop();
numStack.pop();
}
int top() {
return numStack.top();
}
int getMin() {
return minNumStack.top();
}
private:
stack<int> numStack;
stack<int> minNumStack;
};
/**
* Your MinStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MinStack* obj = new MinStack();
* obj->push(x);
* obj->pop();
* int param_3 = obj->top();
* int param_4 = obj->getMin();
*/
leetcode 341: 扁平化嵌套列表迭代器
思路:初始化的时候将列表中的元素倒序入栈。hasNext()中将栈顶元素解析成列表并倒序入栈,直到栈顶元素是数字。next()中弹出栈顶元素。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
/**
* // This is the interface that allows for creating nested lists.
* // You should not implement it, or speculate about its implementation
* class NestedInteger {
* public:
* // Return true if this NestedInteger holds a single integer, rather than a nested list.
* bool isInteger() const;
*
* // Return the single integer that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a single integer
* // The result is undefined if this NestedInteger holds a nested list
* int getInteger() const;
*
* // Return the nested list that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a nested list
* // The result is undefined if this NestedInteger holds a single integer
* const vector<NestedInteger> &getList() const;
* };
*/
class NestedIterator {
public:
NestedIterator(vector<NestedInteger> &nestedList) {
for(int i = nestedList.size()-1; i >= 0; i--) {
st.push(nestedList[i]);
}
}
int next() {
int res = st.top().getInteger();
st.pop();
return res;
}
bool hasNext() {
while(!st.empty()) {
if(st.top().isInteger()) return true;
vector<NestedInteger> nestedList = st.top().getList();
st.pop();
for(int i = nestedList.size()-1; i >= 0; i--) {
st.push(nestedList[i]);
}
}
return false;
}
private:
stack<NestedInteger> st;
};
/**
* Your NestedIterator object will be instantiated and called as such:
* NestedIterator i(nestedList);
* while (i.hasNext()) cout << i.next();
*/
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
/**
* // This is the interface that allows for creating nested lists.
* // You should not implement it, or speculate about its implementation
* class NestedInteger {
* public:
* // Return true if this NestedInteger holds a single integer, rather than a nested list.
* bool isInteger() const;
*
* // Return the single integer that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a single integer
* // The result is undefined if this NestedInteger holds a nested list
* int getInteger() const;
*
* // Return the nested list that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a nested list
* // The result is undefined if this NestedInteger holds a single integer
* const vector<NestedInteger> &getList() const;
* };
*/
class NestedIterator {
public:
NestedIterator(vector<NestedInteger> &nestedList) {
begins.push(nestedList.begin());
ends.push(nestedList.end());
}
int next() {
return (begins.top()++)->getInteger();
}
bool hasNext() {
while(!begins.empty()) {
if(begins.top() == ends.top()) {
begins.pop();
ends.pop();
} else {
auto x = begins.top();
if(x->isInteger()) return true;
begins.top()++; // 为将来退栈后访问到这个节点做准备
begins.push(x->getList().begin());
ends.push(x->getList().end());
}
}
return false;
}
private:
stack<vector<NestedInteger>::iterator> begins, ends;
};
/**
* Your NestedIterator object will be instantiated and called as such:
* NestedIterator i(nestedList);
* while (i.hasNext()) cout << i.next();
*/
剑指 Offer 09. 用两个栈实现队列
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
public class Solution {
Stack<Integer> stack1 = new Stack<Integer>();
Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack<Integer>();
public void push(int node) {
stack1.push(node);
}
public int pop() {
if(stack2.empty()) {
while(!stack1.empty()) {
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
return stack2.pop();
}
}
剑指 Offer 59 - II. 队列的最大值
思路:队列+双端队列deque(队首出队,队尾入栈)
剑指 Offer 59 - I. 滑动窗口的最大值
思路:双端队列deque,去掉队首的窗口以外的数,在队尾入栈,将队首的最大值放进结果中。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] in = {2,3,4,2,6,2,5,1};
System.out.println(maxInWindows(in, 3));
}
public static ArrayList<Integer> maxInWindows(int[] num, int size) {
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (size <= 0) return res;
LinkedList<Integer> index = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
if(!index.isEmpty() && i - size + 1 > index.getFirst()) index.removeFirst();
while (!index.isEmpty() && num[i] >= num[index.peekLast()]) index.removeLast();
index.add(i);
if(i - size + 1 >= 0) res.add(num[index.getFirst()]);
}
return res;
}
}
堆
leetcode 23: 归并K个排序链表
-
方法1:堆(优先队列)
-
时间:$O(N\log K)$,空间:$O(\log K)$
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) { priority_queue<ListNode*, vector<ListNode*>, compare> q; for(auto item: lists) { if(item) q.push(item); } ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0); ListNode* tail = dummy; while(!q.empty()) { tail->next = q.top(); tail = tail->next; q.pop(); if(tail->next) q.push(tail->next); } return dummy->next; } private: struct compare { bool operator()(const ListNode* l, const ListNode* r) { return l->val > r->val; } }; };
-
-
方法2:分治
-
思路:两两合并链表
-
时间:$O(N\log K)$,空间:$O(1)$
-
leetcode 378: 有序矩阵中第K小的数
-
思路:和23题类似,用堆(优先队列)
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23
class Solution { public: int kthSmallest(vector<vector<int>>& matrix, int k) { int rows = matrix.size(); int cols = matrix[0].size(); priority_queue<Position> pq; for(int i = 0; i < rows; i++) { } } private: struct Position { int i; int j; int val; bool operator < (const Position& p) const { return val > p.val; } } };
leetcode 215: 数组中的第K个最大元素
方法1:优先队列,时间$O(N \log K)$,空间$O(\log K)$
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
class Solution {
public:
int findKthLargest(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> pq; // 数字小的优先级大
for(int num: nums) {
pq.push(num);
if(pq.size() > k) {
pq.pop();
}
}
return pq.top();
}
};
方法2:快速排序,时间$O(N \log N)$,空间$O(\log N)$
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
class Solution {
public:
int findKthLargest(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
return nums[nums.size()-k];
}
};
方法3:快速选择,时间$O(N)$,空间$O(1)$
T(N) =n +n/2+n/4+n/8+n/2^k = n*(1-2^-k)/(1-2^-1) =2N
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
class Solution {
public:
int findKthLargest(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
random_shuffle(nums.begin(), nums.end());
k = nums.size() - k;
int lo = 0;
int hi = nums.size() - 1;
while(lo < hi) {
int j = partition(lo, hi, nums);
if(j > k) hi = j - 1;
else if(j < k) lo = j + 1;
else break;
}
return nums[k];
}
private:
int partition(int lo, int hi, vector<int>& nums) {
int i = lo;
int j = hi + 1;
int pivot = nums[lo];
while(true) {
while(nums[++i] < pivot) if(i == hi) break;
while(pivot < nums[--j]) if(j == lo) break;
if(i >= j) break;
swap(nums[i], nums[j]);
}
swap(nums[lo], nums[j]);
return j;
}
};
leetcode 295: 数据流中的中位数
思路:小的一半数放在大顶堆里,大的一半数放在小顶堆里。插入时先插入到小的一半里,再调整一个到大的一半,如果大的一半数量大于小的一半,再调整一个回来,保证小的一半的数量大于等于大的一半。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
class MedianFinder {
public:
/** initialize your data structure here. */
MedianFinder() {
}
void addNum(int num) {
small.push(num);
large.push(small.top());
small.pop();
if(large.size() > small.size()) {
small.push(large.top());
large.pop();
}
}
double findMedian() {
if(small.size() > large.size()) return small.top();
return (small.top() + large.top()) / 2.0;
}
private:
priority_queue<int> small; // 大顶堆
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> large; // 小顶堆
};
/**
* Your MedianFinder object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MedianFinder* obj = new MedianFinder();
* obj->addNum(num);
* double param_2 = obj->findMedian();
*/
树
leetcode 98: 验证二叉搜索树
-
中序遍历
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) { vector<int> result; inorderTraversal(root, result); for(int i = 1; i < result.size(); i++) { if(result[i-1] >= result[i]) return false; } return true; } private: void inorderTraversal(TreeNode *root, vector<int>& result) { if(root == NULL) return; inorderTraversal(root->left, result); result.push_back(root->val); inorderTraversal(root->right, result); } };
-
中序遍历2
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) { TreeNode* prev = NULL; return validate(root, prev); } private: bool validate(TreeNode* root, TreeNode*& prev) { if(root == NULL) return true; if(!validate(root->left, prev)) return false; if(prev && prev->val >= root->val) return false; prev = root; return validate(root->right, prev); } };
-
递归
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) { return isValidBST(root, LONG_MIN, LONG_MAX); } private: bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root, long min, long max) { if(root == NULL) return true; if(root->val <= min) return false; if(root->val >= max) return false; if(!isValidBST(root->left, min, root->val)) return false; return isValidBST(root->right, root->val, max); } };
leetcode 99: 恢复二叉排序树
-
思路:中序遍历
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: void recoverTree(TreeNode* root) { TreeNode* prev = NULL; TreeNode* first = NULL; TreeNode* second = NULL; traverse(root, prev, first, second); int temp = first->val; first->val = second->val; second->val = temp; } private: void traverse(TreeNode* root, TreeNode*& prev, TreeNode*& first, TreeNode*& second) { if(root == NULL) return; traverse(root->left, prev, first, second); if(first == NULL && prev != NULL && prev->val > root->val) first = prev; if(first != NULL && prev != NULL && prev->val > root->val) second = root; prev = root; traverse(root->right, prev, first, second); } };
leetcode 100: 相同的树
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: bool isSameTree(TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) { if(p == NULL && q == NULL) return true; if(p == NULL || q == NULL) return false; if(p->val == q->val && isSameTree(p->left, q->left) && isSameTree(p->right, q->right)) return true; return false; } };
leetcode 101: 对称二叉树
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) { if(root == NULL) return true; return isSymmetric(root->left, root->right); } private: bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* left, TreeNode* right) { if(left == NULL && right == NULL) return true; if(left == NULL || right == NULL) return false; if(left->val == right->val && isSymmetric(left->left, right->right) && isSymmetric(left->right, right->left)) return true; return false; } };
[leetcode 103: 二叉树的锯齿形层次遍历]
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode* root) { vector<vector<int>> res; if(root == NULL) return res; queue<TreeNode*> q; q.push(root); bool inOrder = true; while(!q.empty()) { vector<int> levelNodes; int queueSize = q.size(); while(queueSize--) { TreeNode* root = q.front(); q.pop(); levelNodes.push_back(root->val); if(root->left != NULL) q.push(root->left); if(root->right != NULL) q.push(root->right); } if(!inOrder) reverse(levelNodes.begin(), levelNodes.end()); inOrder = !inOrder; res.push_back(levelNodes); } return res; } };
leetcode 104: 二叉数的最大深度
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) { if(root == NULL) return 0; return 1+max(maxDepth(root->left), maxDepth(root->right)); } };
leetcode 105: 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) { return buildTree(0, preorder.size(), 0, inorder.size(), preorder, inorder); } private: TreeNode* buildTree(int preBegin, int preEnd, int inBegin, int inEnd, vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) { if(preEnd - preBegin == 0) return NULL; if(preEnd - preBegin == 1) return new TreeNode(preorder[preBegin]); int rootVal = preorder[preBegin]; int rootIdx; for(int i = inBegin; i < inEnd; i++) { if(inorder[i] == rootVal) { rootIdx = i; break; } } TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootVal); root->left = buildTree(preBegin+1, preBegin+1+rootIdx-inBegin, inBegin, rootIdx, preorder, inorder); root->right = buildTree(preBegin+1+rootIdx-inBegin, preEnd, rootIdx+1, inEnd, preorder, inorder); return root; } };
leetcode 106: 从后序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) { return buildTree(0, inorder.size(), 0, postorder.size(), inorder, postorder); } private: TreeNode* buildTree(int inBegin, int inEnd, int postBegin, int postEnd, vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) { if(postEnd - postBegin == 0) return NULL; if(postEnd - postBegin == 1) return new TreeNode(postorder[postEnd-1]); int rootVal = postorder[postEnd-1]; int rootIdx; for(int i = inBegin; i < inEnd; i++) { if(inorder[i] == rootVal) { rootIdx = i; break; } } TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootVal); root->left = buildTree(inBegin, rootIdx, postBegin, rootIdx+postBegin-inBegin, inorder, postorder); root->right = buildTree(rootIdx+1, inEnd, rootIdx+postBegin-inBegin, postEnd-1, inorder, postorder); return root; } };
leetcode 108: 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: TreeNode* sortedArrayToBST(vector<int>& nums) { return sortedArrayToBST(nums, 0, nums.size()); } private: TreeNode* sortedArrayToBST(vector<int>& nums, int lo, int hi) { if(lo == hi) return NULL; int mid = (lo + hi) / 2; TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]); root->left = sortedArrayToBST(nums, lo, mid); root->right = sortedArrayToBST(nums, mid+1, hi); return root; } };
[leetcode 109: 有序链表转换二叉搜索树]
-
时间:$O(n \log n)$
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: TreeNode* sortedListToBST(ListNode* head) { return sortedListToBST(head, NULL); } private: TreeNode* sortedListToBST(ListNode* head, ListNode* tail) { if(head == tail) return NULL; ListNode* fast = head; ListNode* slow = head; while(fast != tail && fast->next != tail) { fast = fast->next->next; slow = slow->next; } TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(slow->val); root->left = sortedListToBST(head, slow); root->right = sortedListToBST(slow->next, tail); return root; } };
leetcode 110: 平衡二叉树
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) { bool res = true; maxDepth(root, res); return res; } private: int maxDepth(TreeNode* root, bool& res) { if(root == NULL) return 0; int leftMaxDepth = maxDepth(root->left, res); int rightMaxDepth = maxDepth(root->right, res); if(abs(leftMaxDepth-rightMaxDepth) > 1) res = false; return 1 + max(leftMaxDepth, rightMaxDepth); } };
leetcode 111: 二叉树的最小深度
-
方法1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: int minDepth(TreeNode* root) { if(root == NULL) return 0; int res = INT_MAX; minDepth(root, 1, res); return res; } private: void minDepth(TreeNode* root, int depth, int& res) { if(root == NULL) return; if(root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL) res = min(res, depth); minDepth(root->left, depth+1, res); minDepth(root->right, depth+1, res); } };
-
方法2
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: int minDepth(TreeNode* root) { if(root == NULL) return 0; if(root->left == NULL) return 1 + minDepth(root->right); if(root->right == NULL) return 1 + minDepth(root->left); return 1 + min(minDepth(root->left), minDepth(root->right)); } };
leetcode 112: 路径总和
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) { if(root == NULL) return false; return traverse(root, sum); } private: bool traverse(TreeNode* root, int sum) { sum -= root->val; if(root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL && sum == 0) return true; if(root->left != NULL && traverse(root->left, sum)) return true; if(root->right != NULL && traverse(root->right, sum)) return true; return false; } }; /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) { if(root == NULL) return false; if(root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL && sum-root->val == 0) return true; return (hasPathSum(root->left, sum-root->val) || hasPathSum(root->right, sum-root->val)); } };
leetcode 113: 路径总和II
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) { vector<vector<int>> res; vector<int> path; pathSum(root, sum, path, res); return res; } private: void pathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum, vector<int>& path, vector<vector<int>>& res) { if(root == NULL) return; path.push_back(root->val); if(root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL && sum-root->val == 0) { res.push_back(path); path.pop_back(); //don't forget to remove the last integer return; } pathSum(root->left, sum-root->val, path, res); pathSum(root->right, sum-root->val, path, res); path.pop_back(); } };
leetcode 114: 二叉树展开为链表
-
方法1:先序遍历,但是展开为链表会破坏结点的右子树,所以递归过程中要把左右子树的指针先保存起来
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: void flatten(TreeNode* root) { TreeNode* dummy = new TreeNode(0); TreeNode* prev = dummy; traverse(root, prev); } private: void traverse(TreeNode* root, TreeNode*& prev) { if(root == NULL) return; TreeNode* left = root->left; TreeNode* right = root->right; prev->left = NULL; prev->right = root; prev = root; traverse(left, prev); traverse(right, prev); } };
-
方法2:先序遍历翻转
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
private TreeNode prev = null; public void flatten(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) return; flatten(root.right); flatten(root.left); root.right = prev; root.left = null; prev = root; }
leetcode 116: 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
-
方法1:层次遍历
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44
/* // Definition for a Node. class Node { public: int val; Node* left; Node* right; Node* next; Node() {} Node(int _val, Node* _left, Node* _right, Node* _next) { val = _val; left = _left; right = _right; next = _next; } }; */ class Solution { public: Node* connect(Node* root) { if(root == NULL) return NULL; queue<Node*> q; q.push(root); while(!q.empty()) { vector<Node*> levelNodes; int levelSize = q.size(); while(levelSize--) { Node* root = q.front(); q.pop(); levelNodes.push_back(root); if(root->left != NULL) q.push(root->left); if(root->right != NULL) q.push(root->right); } for(int i = 0; i < levelNodes.size()-1; i++) { levelNodes[i]->next = levelNodes[i+1]; } levelNodes[levelNodes.size()-1] = NULL; } return root; } };
-
方法2
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
// https://leetcode.com/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node/discuss/37472/A-simple-accepted-solution void connect(TreeLinkNode *root) { if (root == NULL) return; TreeLinkNode *pre = root; TreeLinkNode *cur = NULL; while(pre->left) { cur = pre; while(cur) { cur->left->next = cur->right; if(cur->next) cur->right->next = cur->next->left; cur = cur->next; } pre = pre->left; } }
leetcode 117: 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针II
-
方法1:层次遍历
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44
/* // Definition for a Node. class Node { public: int val; Node* left; Node* right; Node* next; Node() {} Node(int _val, Node* _left, Node* _right, Node* _next) { val = _val; left = _left; right = _right; next = _next; } }; */ class Solution { public: Node* connect(Node* root) { if(root == NULL) return NULL; queue<Node*> q; q.push(root); while(!q.empty()) { int levelSize = q.size(); vector<Node*> levelNodes; while(levelSize--) { Node* node = q.front(); q.pop(); levelNodes.push_back(node); if(node->left != NULL) q.push(node->left); if(node->right != NULL) q.push(node->right); } for(int i = 0; i < levelNodes.size()-1; i++) { levelNodes[i]->next = levelNodes[i+1]; } levelNodes[levelNodes.size()-1]->next = NULL; } return root; } };
leetcode 124: 二叉树中的最大路径和
-
思路:迭代过程中,得到每个结点的左子树最大路径和与右子树最大路径和,更新结果,返回这个结点为根节点的子树的最大路径和。
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: int maxPathSum(TreeNode* root) { int res = INT_MIN; maxPathSum(root, res); return res; } int maxPathSum(TreeNode* root, int& res) { if(root == NULL) return 0; int left = max(0, maxPathSum(root->left, res)); int right = max(0, maxPathSum(root->right, res)); int sum = root->val + left + right; res = max(sum, res); return root->val + max(left, right); } };
leetcode 543: 二叉树的直径
思路:跟上面这题差不多
leetcode 208: 实现 Trie (前缀树)
方法1:迭代
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
class Trie {
public:
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
Trie() {
root = new TrieNode(' ');
}
/** Inserts a word into the trie. */
void insert(string word) {
insert(root, 0, word);
}
/** Returns if the word is in the trie. */
bool search(string word) {
return search(root, 0, word);
}
/** Returns if there is any word in the trie that starts with the given prefix. */
bool startsWith(string prefix) {
return startsWith(root, 0, prefix);
}
private:
// https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trie
struct TrieNode {
char val;
bool end;
unordered_map<char, TrieNode*> neighbours;
TrieNode(char _val): val(val), end(false) {};
};
TrieNode* root;
void insert(TrieNode* root, int cur, string& word) {
if(cur == word.length()) {
root->end = true;
return;
}
if(!root->neighbours.count(word[cur])) {
root->neighbours[word[cur]] = new TrieNode(word[cur]);
}
insert(root->neighbours[word[cur]], cur+1, word);
}
bool search(TrieNode* root, int cur, string& word) {
if(cur == word.length() && root->end) return true;
if(root->neighbours.count(word[cur])) {
return search(root->neighbours[word[cur]], cur+1, word);
}
return false;
}
bool startsWith(TrieNode* root, int cur, string& word) {
if(cur == word.length()) return true;
if(root->neighbours.count(word[cur])) {
return startsWith(root->neighbours[word[cur]], cur+1, word);
}
return false;
}
};
/**
* Your Trie object will be instantiated and called as such:
* Trie* obj = new Trie();
* obj->insert(word);
* bool param_2 = obj->search(word);
* bool param_3 = obj->startsWith(prefix);
*/
方法2:迭代
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
class Trie {
public:
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
Trie() {
root = new TrieNode(' ');
}
/** Inserts a word into the trie. */
void insert(string word) {
TrieNode* node = root;
for(int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
if(!node->neighbours.count(word[i])) {
node->neighbours[word[i]] = new TrieNode(word[i]);
}
node = node->neighbours[word[i]];
}
node->end = true;
}
/** Returns if the word is in the trie. */
bool search(string word) {
TrieNode* node = root;
for(int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
if(!node->neighbours.count(word[i])) return false;
node = node->neighbours[word[i]];
}
return node->end == true;
}
/** Returns if there is any word in the trie that starts with the given prefix. */
bool startsWith(string prefix) {
TrieNode* node = root;
for(int i = 0; i < prefix.length(); i++) {
if(!node->neighbours.count(prefix[i])) return false;
node = node->neighbours[prefix[i]];
}
return true;
}
private:
// https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trie
struct TrieNode {
char val;
bool end;
map<char, TrieNode*> neighbours;
TrieNode(char _val): val(val), end(false) {};
};
TrieNode* root;
};
/**
* Your Trie object will be instantiated and called as such:
* Trie* obj = new Trie();
* obj->insert(word);
* bool param_2 = obj->search(word);
* bool param_3 = obj->startsWith(prefix);
*/
leetcode 212: 单词搜索II
方法1:dfs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> findWords(vector<vector<char>>& board, vector<string>& words) {
int rows = board.size();
if(rows == 0) return vector<string>();
int cols = board[0].size();
if(cols == 0) return vector<string>();
unordered_set<string> res;
vector<vector<bool>> visited(rows, vector<bool>(cols, false));
for(int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
for(string word: words) {
dfs(i, j, rows, cols, board, visited, 0, word, res);
}
}
}
vector<string> vec;
for(string s: res) {
vec.push_back(s);
}
return vec;
}
private:
void dfs(int i, int j, int rows, int cols, vector<vector<char>>& board, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int cur, string& word, unordered_set<string>& res) {
if(board[i][j] != word[cur]) return;
if(cur == word.length()-1) {
res.insert(word);
return;
}
visited[i][j] = true;
if(i-1 >= 0 && !visited[i-1][j]) dfs(i-1, j, rows, cols, board, visited, cur+1, word, res);
if(i+1 < rows && !visited[i+1][j]) dfs(i+1, j, rows, cols, board, visited, cur+1, word, res);
if(j-1 >= 0 && !visited[i][j-1]) dfs(i, j-1, rows, cols, board, visited, cur+1, word, res);
if(j+1 < cols && !visited[i][j+1]) dfs(i, j+1, rows, cols, board, visited, cur+1, word, res);
visited[i][j] = false;
}
};
方法2:dfs+trie
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> findWords(vector<vector<char>>& board, vector<string>& words) {
// build trie
TrieNode* root = new TrieNode(' ');
for(string word: words) {
TrieNode* node = root;
for(int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
if(!node->neighbours.count(word[i])) {
node->neighbours[word[i]] = new TrieNode(word[i]);
}
node = node->neighbours[word[i]];
}
node->wordEnd = true;
}
// backtrack
int rows = board.size();
int cols = board[0].size();
vector<vector<bool>> visited(rows, vector<bool>(cols, false));
unordered_set<string> res;
for(int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
dfs(i, j, rows, cols, board, visited, root, "", res);
}
}
vector<string> vec;
for(string s: res) {
vec.push_back(s);
}
return vec;
}
private:
struct TrieNode {
char val;
unordered_map<char, TrieNode*> neighbours;
bool wordEnd;
TrieNode(char _val): val(_val), wordEnd(false) {};
};
void dfs(int i, int j, int rows, int cols, vector<vector<char>>& board, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, TrieNode* root, string word, unordered_set<string>& res) {
if(!root->neighbours.count(board[i][j])) return;
TrieNode* child = root->neighbours[board[i][j]];
word += board[i][j];
if(child->wordEnd) {
res.insert(word);
// cannot return
}
visited[i][j] = true;
if(i-1 >= 0 && !visited[i-1][j]) dfs(i-1, j, rows, cols, board, visited, child, word, res);
if(i+1 < rows && !visited[i+1][j]) dfs(i+1, j, rows, cols, board, visited, child, word, res);
if(j-1 >= 0 && !visited[i][j-1]) dfs(i, j-1, rows, cols, board, visited, child, word, res);
if(j+1 < cols && !visited[i][j+1]) dfs(i, j+1, rows, cols, board, visited, child, word, res);
visited[i][j] = false;
}
};
leetcode 235: 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
思路:如果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root.val < p.val && root.val < q.val)
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
if(root.val > p.val && root.val > q.val)
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
return root;
}
}
leetcode 236: 二叉树的最近公共祖先
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
unordered_map<TreeNode*, TreeNode*> father;
father[root] = NULL;
traverse(root, father);
vector<TreeNode*> path1;
vector<TreeNode*> path2;
while(p != NULL) {
path1.push_back(p);
p = father[p];
}
while(q != NULL) {
path2.push_back(q);
q = father[q];
}
int i = path1.size() - 1;
int j = path2.size() - 1;
while(i >= 0 && j >= 0 && path1[i] == path2[j]) {
i--;
j--;
}
return path1[i+1];
}
private:
void traverse(TreeNode* root, unordered_map<TreeNode*, TreeNode*>& father) {
if(root->left != NULL) {
father[root->left] = root;
traverse(root->left, father);
}
if(root->right != NULL) {
father[root->right] = root;
traverse(root->right, father);
}
}
};
这个函数的功能有三个:给定两个节点 p 和 q
- 如果 p 和 q 都存在,则返回它们的公共祖先;
- 如果只存在一个,则返回存在的一个;
- 如果 p 和 q 都不存在,则返回NULL
如果left是NULL返回right,如果right是NULL返回left,如果都不是NULL返回root。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(root == NULL)
return NULL;
if(root == p || root == q)
return root;
TreeNode* left = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
TreeNode* right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
if(left == NULL)
return right;
if(right == NULL)
return left;
if(left && right) // p和q在两侧
return root;
return NULL; // 必须有返回值
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if (!root || root == p || root == q) return root;
TreeNode* left = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
TreeNode* right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
return !left ? right : !right ? left : root;
}
leetcode 144: 二叉树的先序遍历
-
思路:先访问结点,将右子树入栈,向左子树追溯;然后出栈
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
class Solution { public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { while(true) { while(root != null) { res.add(root.val); stack.push(root.right); root = root.left; } if(stack.empty()) break; root = stack.pop(); } return res; } private Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>(); private List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); }
leetcode 94: 二叉树的中序遍历
-
思路:先入栈并往左子树追溯;然后出栈,访问结点,转入右子树。
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
class Solution { public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { while(true) { while(root != null) { stack.push(root); root = root.left; } if(stack.empty()) break; root = stack.pop(); res.add(root.val); root = root.right; } return res; } private Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>(); private List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); }
leetcode 145: 二叉树的后序遍历
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
while(true) {
while(root != null) {
res.add(root.val);
stack.push(root.left);
root = root.right;
}
if(stack.empty()) break;
root = stack.pop();
}
Collections.reverse(res);
return res;
}
private Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
private List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
}
Here I summarize the iterative implementation for preorder, inorder, and postorder traverse.
Pre Order Traverse
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new ArrayDeque<>();
TreeNode p = root;
while(!stack.isEmpty() || p != null) {
if(p != null) {
stack.push(p);
result.add(p.val); // Add before going to children
p = p.left;
} else {
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
p = node.right;
}
}
return result;
}
In Order Traverse
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new ArrayDeque<>();
TreeNode p = root;
while(!stack.isEmpty() || p != null) {
if(p != null) {
stack.push(p);
p = p.left;
} else {
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
result.add(node.val); // Add after all left children
p = node.right;
}
}
return result;
}
Post Order Traverse
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
LinkedList<Integer> result = new LinkedList<>();
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new ArrayDeque<>();
TreeNode p = root;
while(!stack.isEmpty() || p != null) {
if(p != null) {
stack.push(p);
result.addFirst(p.val); // Reverse the process of preorder
p = p.right; // Reverse the process of preorder
} else {
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
p = node.left; // Reverse the process of preorder
}
}
return result;
}
leetcode 230: 二叉搜索树中的第K小的元素
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int kthSmallest(TreeNode* root, int k) {
int res;
inOrderTraverse(root, k, res);
return res;
}
private:
bool inOrderTraverse(TreeNode* root, int& k, int& res) {
if(root == NULL) return false;
if(inOrderTraverse(root->left, k, res)) return true;
if(--k == 0) {
res = root->val;
return true;
}
if(inOrderTraverse(root->right, k, res)) return true;
return false;
}
};
leetcode 297: 二叉树的序列化与反序列化
层次遍历
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Codec {
public:
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
string serialize(TreeNode* root) {
vector<string> res;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = q.front();
q.pop();
res.push_back(node==NULL? "null": to_string(node->val));
if(node != NULL) {
q.push(node->left);
q.push(node->right);
}
}
string serializeStr;
for(int i = 0; i < res.size(); i++) {
serializeStr += res[i] + ' ';
}
cout << serializeStr << endl;
return serializeStr;
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
TreeNode* deserialize(string data) {
stringstream ss(data);
string val;
vector<TreeNode*> vec;
while(ss >> val) {
if(val == "null") vec.push_back(NULL);
else vec.push_back(new TreeNode(stoi(val)));
}
if(vec[0] == NULL) return NULL;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(vec[0]);
int cur = 1;
while(!q.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = q.front();
q.pop();
TreeNode* left = vec[cur++];
node->left = left;
if(left != NULL) q.push(left);
TreeNode* right = vec[cur++];
node->right = right;
if(right != NULL) q.push(right);
}
return vec[0];
}
};
递归
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Codec {
public:
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
string serialize(TreeNode* root) {
ostringstream out;
serialize(root, out);
return out.str();
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
TreeNode* deserialize(string data) {
istringstream in(data);
return deserialize(in);
}
private:
void serialize(TreeNode* root, ostringstream& out) {
if(root == NULL) out << "n ";
else {
out << root->val << " ";
serialize(root->left, out);
serialize(root->right, out);
}
}
TreeNode* deserialize(istringstream& in) {
string val;
in >> val;
if(val == "n") return NULL;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(stoi(val));
root->left = deserialize(in);
root->right = deserialize(in);
return root;
}
};
剑指 Offer 26. 树的子结构
思路:对于A树的每个节点,判断该节点为根节点的子树是否包含B树。
链表
leetcode 19: 删除链表的倒数第N个节点
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ /** * 0 1 2 3 4 5 * dummy head * left right * left right * * 0 1 * dummy head * left right */ class Solution { public: ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) { ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0); dummy->next = head; ListNode* left = dummy; ListNode* right = dummy; for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { right = right->next; } while(right->next != NULL) { left = left->next; right = right->next; } ListNode* p = left->next; left->next = p->next; delete(p); return dummy->next; } };
leetcode 24: 两两交换链表中的节点
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) { ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0); dummy->next = head; ListNode* prev = dummy; ListNode* tail = dummy; for(int i = 0; i < 2; i++) { tail = tail->next; if(tail == NULL) return dummy->next; } while(true) { ListNode* temp = prev->next; prev->next = tail; temp->next = tail->next; tail->next = temp; for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { tail = tail->next; if(tail == NULL) return dummy->next; } for(int i = 0; i < 2; i++) { prev = prev->next; } } return dummy->next; } };
leetcode 25: K个一组翻转链表
-
思路:先往后遍历K个结点,如果中途链表没有结束,就翻转这些结点。
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ /* * 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 * dummy head * prev * tail * * 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 * dummy tail * prev * * 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 * dummy temp tail * prev * * 0 2 3 4 1 5 6 7 8 9 * dummy tail temp * prev * * 0 4 3 2 1 5 6 7 8 9 * dummy tail * prev */ class Solution { public: ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) { ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0); dummy->next = head; ListNode* prev = dummy; ListNode* tail = dummy; for(int i = 0; i < k; i++) { tail = tail->next; if(tail == NULL) return dummy->next; } while(true) { for(int i = 0; i < k-1; i++) { ListNode* temp = prev->next; prev->next = temp->next; temp->next = tail->next; tail->next = temp; } for(int i = 0; i < 2*k-1; i++) { tail = tail->next; if(tail == NULL) return dummy->next; } for(int i = 0; i < k; i++) { prev = prev->next; } } return dummy->next; } };
leetcode 61: 旋转链表
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* rotateRight(ListNode* head, int k) { if(head == NULL) return head; // find tail pointer int numNode = 1; ListNode* tail = head; while(tail->next != NULL) { tail = tail->next; numNode++; } cout << numNode; // find pointer int step = numNode - 1 - k % numNode; ListNode* p = head; for(int i = 0; i < step; i++) { p = p->next; } ListNode* next = p->next; if(next == NULL) { // do not change return head; } else { // rotate tail->next = head; p->next = NULL; return next; } } };
leetcode 82: 删除排序链表中的重复元素II
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) { ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0); dummy->next = head; ListNode* pre = dummy; ListNode* p = head; while(p != NULL) { if(p->next != NULL && p->val == p->next->val) { // delete this number int val = p->val; while(p != NULL && p->val == val) { pre->next = p->next; delete(p); p = pre->next; } } else { pre = p; p = p->next; } } return dummy->next; } };
leetcode 83: 删除排序链表中的重复元素
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) { if(head == NULL) return NULL; ListNode* cur = head; int lastVal = cur->val; while(cur->next != NULL) { ListNode* tmp = cur->next; if(tmp->val == lastVal) { cur->next = tmp->next; delete(tmp); } else { lastVal = tmp->val; cur = cur->next; } } return head; } };
leetcode 92: 翻转链表
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* reverseBetween(ListNode* head, int m, int n) { if(m == n) return head; ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0); dummy->next = head; // 1->2->3->4->5->NULL, m = 2, n = 4 // left: 1, p: 2 ListNode* left = dummy; ListNode* p = head; for(int i = 0; i < m-1; i++) { left = p; p = p->next; } // reverse list // left: 1, start: 2, p: 4, right: 5 ListNode* start = p; ListNode* pre = p; p = p->next; for(int i = 0; i < n-m-1; i++) { ListNode* next = p->next; p->next = pre; pre = p; p = next; } ListNode* right = p->next; p->next = pre; // connect together left->next = p; start->next = right; return dummy->next; } };
leetcode 138: 复制带随机指针的链表
-
方法1:用散列表记录原链表结点到新链表结点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46
/* // Definition for a Node. class Node { public: int val; Node* next; Node* random; Node() {} Node(int _val, Node* _next, Node* _random) { val = _val; next = _next; random = _random; } }; */ class Solution { public: Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) { Node* cur = head; Node* copyDummy = new Node(0, NULL, NULL); Node* copyPrev = copyDummy; unordered_map<Node*, Node*> map; while(cur != NULL) { Node* p = new Node(cur->val, NULL, NULL); copyPrev->next = p; copyPrev = p; map[cur] = p; cur = cur->next; } cur = head; Node* copyCur = copyDummy->next; while(cur != NULL) { copyCur->random = map[cur->random]; cur = cur->next; copyCur = copyCur->next; } return copyDummy->next; } };
-
方法2:原结点和新节点交替,更新新节点的random指针,分开两个链表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62
/* // Definition for a Node. class Node { public int val; public Node next; public Node random; public Node() {} public Node(int _val,Node _next,Node _random) { val = _val; next = _next; random = _random; } }; */ public class Solution { public Node copyRandomList(Node head) { if (head == null) { return null; } // Creating a new weaved list of original and copied nodes. Node ptr = head; while (ptr != null) { // Cloned node Node newNode = new Node(ptr.val); // Inserting the cloned node just next to the original node. // If A->B->C is the original linked list, // Linked list after weaving cloned nodes would be A->A'->B->B'->C->C' newNode.next = ptr.next; ptr.next = newNode; ptr = newNode.next; } ptr = head; // Now link the random pointers of the new nodes created. // Iterate the newly created list and use the original nodes' random pointers, // to assign references to random pointers for cloned nodes. while (ptr != null) { ptr.next.random = (ptr.random != null) ? ptr.random.next : null; ptr = ptr.next.next; } // Unweave the linked list to get back the original linked list and the cloned list. // i.e. A->A'->B->B'->C->C' would be broken to A->B->C and A'->B'->C' Node ptr_old_list = head; // A->B->C Node ptr_new_list = head.next; // A'->B'->C' Node head_old = head.next; while (ptr_old_list != null) { ptr_old_list.next = ptr_old_list.next.next; ptr_new_list.next = (ptr_new_list.next != null) ? ptr_new_list.next.next : null; ptr_old_list = ptr_old_list.next; ptr_new_list = ptr_new_list.next; } return head_old; } }
leetcode 141: 环形链表
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {
if(head == NULL) return false;
ListNode* walker = head;
ListNode* runner = head;
while(runner != NULL && runner->next != NULL) {
walker = walker->next;
runner = runner->next->next;
if(walker == runner) return true;
}
return false;
}
};
leetcode 142: 环形链表
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
ListNode* fast = head;
ListNode* slow = head;
while(fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if(slow == fast) {
ListNode* p = head;
while(p != slow) {
p = p->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return p;
}
}
return NULL;
}
};
leetcode 143: 重排链表
思路:翻转后半个链表。
leetcode 146: LRU缓存机制
方法1:双向链表+hashmap,自己实现双向链表。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
class LRUCache {
public:
LRUCache(int capacity) {
headDummy = new ListNode(0, 0);
tailDummy = new ListNode(0, 0);
headDummy->prev = tailDummy;
tailDummy->next = headDummy;
size = 0;
this->capacity = capacity;
}
int get(int key) {
if(map.find(key) != map.end()) {
ListNode* node = map[key];
int value = node->val;
deleteKey(key);
push(key, value);
return value;
}
return -1;
}
void put(int key, int value) {
if(map.find(key) != map.end()) {
deleteKey(key);
push(key, value);
} else {
if(size < capacity) {
size++;
} else {
pop();
}
push(key, value);
}
}
private:
struct ListNode {
int key;
int val;
ListNode* next;
ListNode* prev;
ListNode(int x, int y): key(x), val(y), next(NULL), prev(NULL) {}
};
unordered_map<int, ListNode*> map;
ListNode* headDummy;
ListNode* tailDummy;
int size;
int capacity;
void push(int key, int value) {
ListNode* node = new ListNode(key, value);
map[key] = node;
ListNode* next = tailDummy->next;
tailDummy->next = node;
node->next = next;
next->prev = node;
node->prev = tailDummy;
}
void pop() {
ListNode* node = headDummy->prev;
int key = node->key;
map.erase(key);
ListNode* prev = node->prev;
prev->next = headDummy;
headDummy->prev = prev;
delete(node);
}
void deleteKey(int key) {
ListNode* node = map[key];
map.erase(key);
ListNode* prev = node->prev;
ListNode* next = node->next;
prev->next = next;
next->prev = prev;
delete(node);
}
};
方法2:LinkedHashMap
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
/**
* Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* LRUCache obj = new LRUCache(capacity);
* int param_1 = obj.get(key);
* obj.put(key,value);
*/
class LRUCache {
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
map = new LinkedHashMap<Integer, Integer>(capacity, 0.75f, true) {
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry eldest) {
return size() > capacity;
}
};
}
public int get(int key) {
return map.getOrDefault(key, -1);
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
map.put(key, value);
}
private int capacity;
private LinkedHashMap<Integer, Integer> map;
}
leetcode 147: 对链表进行插入排序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* insertionSortList(ListNode* head) {
if(head == NULL) return head;
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode* insert = head;
while(insert != NULL) {
ListNode* prev = dummy;
ListNode* next = insert->next;
while(prev->next != NULL && prev->next->val <= insert->val) {
prev = prev->next;
}
insert->next = prev->next;
prev->next = insert;
insert = next;
}
return dummy->next;
}
};
leetcode 148: 排序链表
方法1:快速排序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {
return quickSort(head, NULL);
}
private:
ListNode* quickSort(ListNode* head, ListNode* tail) {
if(head == tail) return head;
ListNode* leftDummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode* leftPrev = leftDummy;
ListNode* prev = head;
ListNode* p = head->next;
while(p != tail) {
ListNode* next = p->next;
if(p->val < head->val) {
leftPrev->next = p;
leftPrev = p;
prev->next = next;
p = next;
} else {
prev = prev->next;
p = next;
}
}
leftPrev->next = head;
leftDummy->next = quickSort(leftDummy->next, head);
head->next = quickSort(head->next, tail);
return leftDummy->next;
}
};
方法2:归并排序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {
if(head == NULL || head->next == NULL) return head;
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head;
ListNode* prev = NULL;
while(fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL) {
prev = slow;
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
prev->next = NULL;
ListNode* l1 = sortList(head);
ListNode* l2 = sortList(slow);
return merge(l1, l2);
}
private:
ListNode* merge(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode* prev = dummy;
while(l1 != NULL && l2 != NULL) {
if(l1->val <= l2->val) {
prev->next = l1;
prev = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
} else {
prev->next = l2;
prev = l2;
l2 = l2->next;
}
}
if(l1 != NULL) {
prev->next = l1;
}
if(l2 != NULL) {
prev->next = l2;
}
return dummy->next;
}
};
方法3:自底向上的归并排序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {
if(head == NULL || head->next == NULL) return head;
int length = 0;
ListNode* cur = head;
while(cur != NULL) {
length++;
cur = cur->next;
}
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy->next = head;
for(int step = 1; step < length; step *= 2) {
ListNode* prev = dummy;
ListNode* cur = dummy->next;
while(cur != NULL) {
ListNode* left = cur;
ListNode* right = split(left, step);
cur = split(right, step);
prev = merge(left, right, prev);
}
}
return dummy->next;
}
private:
ListNode* split(ListNode* head, int step) {
ListNode* cur = head;
for(int i = 0; i < step-1 && cur != NULL; i++) {
cur = cur->next;
}
if(cur == NULL) return NULL;
ListNode* second = cur->next;
cur->next = NULL;
return second;
}
ListNode* merge(ListNode* left, ListNode* right, ListNode* prev) {
while(left != NULL && right != NULL) {
if(left->val < right->val) {
prev->next = left;
prev = left;
left = left->next;
} else {
prev->next = right;
prev = right;
right = right->next;
}
}
if(left != NULL) {
prev->next = left;
}
if(right != NULL) {
prev->next = right;
}
while(prev->next != NULL) {
prev = prev->next;
}
return prev;
}
};
leetcode 160: 相交链表
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
ListNode* a = headA;
ListNode* b = headB;
while(a != b) {
a = a == NULL? headB: a->next;
b = b == NULL? headA: b->next;
}
return a;
}
};
leetcode 206: 反转链表
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode* cur = head;
while(cur) {
ListNode* next = cur->next;
cur->next = dummy->next;
dummy->next = cur;
cur = next;
}
return dummy->next;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode p = reverseList(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return p;
}
leetcode 234: 回文链表
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isPalindrome(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head;
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0);
while(fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL) {
fast = fast->next->next;
ListNode* slowNext = slow->next;
slow->next = dummy->next;
dummy->next = slow;
slow = slowNext;
}
ListNode* left = dummy->next;
ListNode* right = fast==NULL? slow: slow->next;
while(left != NULL && right != NULL) {
if(left->val != right->val) return false;
left = left->next;
right = right->next;
}
return true;
}
};
leetcode 237: 删除链表中的节点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
void deleteNode(ListNode* node) {
node->val = node->next->val;
node->next = node->next->next;
}
};
图
leetcode 79: 单词搜索
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47
class Solution { public: bool exist(vector<vector<char>>& board, string word) { int m = board.size(); int n = board[0].size(); vector<vector<bool>> used(m, vector<bool>(n, false)); for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) { for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) { used[i][j] = true; if(backtrack(i, j, 0, m, n, used, board, word)) return true; used[i][j] = false; } } return false; } private: bool backtrack(int i, int j, int cur, int m, int n, vector<vector<bool>>& used, vector<vector<char>>& board, string word) { if(word[cur] != board[i][j]) return false; if(cur == word.length()-1) return true; // go left if(i-1 >= 0 && used[i-1][j] == false) { used[i-1][j] = true; if(backtrack(i-1, j, cur+1, m, n, used, board, word)) return true; used[i-1][j] = false; } // go right if(i+1 < m && used[i+1][j] == false) { used[i+1][j] = true; if(backtrack(i+1, j, cur+1, m, n, used, board, word)) return true; used[i+1][j] = false; } // go down if(j-1 >= 0 && used[i][j-1] == false) { used[i][j-1] = true; if(backtrack(i, j-1, cur+1, m, n, used, board, word)) return true; used[i][j-1] = false; } // go up if(j+1 < n && used[i][j+1] == false) { used[i][j+1] = true; if(backtrack(i, j+1, cur+1, m, n, used, board, word)) return true; used[i][j+1] = false; } return false; } };
leetcode 130: 被围绕的区域
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
class Solution {
public:
void solve(vector<vector<char>>& board) {
int row = board.size();
if(row == 0) return;
int col = board[0].size();
if(col == 0) return;
// 'O' on edge => '@'
vector<vector<bool>> visited(row, vector(col, false));
for(int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
if(!visited[i][0] && board[i][0] == 'O') {
dfs(i, 0, row, col, board, visited);
}
if(board[i][col-1] == 'O') {
dfs(i, col-1, row, col, board, visited);
}
}
for(int j = 1; j < col-1; j++) {
if(board[0][j] == 'O') {
dfs(0, j, row, col, board, visited);
}
if(board[row-1][j] == 'O') {
dfs(row-1, j, row, col, board, visited);
}
}
// 'O' => 'X'
for(int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
if(board[i][j] == 'O') {
board[i][j] = 'X';
}
}
}
// '@' => 'O'
for(int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
if(board[i][j] == '@') {
board[i][j] = 'O';
}
}
}
}
private:
void dfs(int i, int j, int row, int col, vector<vector<char>>& board, vector<vector<bool>>& visited) {
// cout << i << " " << j << endl;
board[i][j] = '@';
visited[i][j] = true;
if(i-1 >= 0 && !visited[i-1][j] && board[i-1][j] == 'O') {
dfs(i-1, j, row, col, board, visited);
}
if(i+1 < row && !visited[i+1][j] && board[i+1][j] == 'O') {
dfs(i+1, j, row, col, board, visited);
}
if(j-1 >= 0 && !visited[i][j-1] && board[i][j-1] == 'O') {
dfs(i, j-1, row, col, board, visited);
}
if(j+1 < col && !visited[i][j+1] && board[i][j+1] == 'O') {
dfs(i, j+1, row, col, board, visited);
}
}
};
leetcode 133: 克隆图
思路:用散列表存储原始图到克隆图结点的映射。DFS过程中,如果克隆结点存在直接返回克隆结点;如果克隆结点不存在,新建克隆结点,递归地得到临界点并连接。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
vector<Node*> neighbors;
Node() {}
Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _neighbors) {
val = _val;
neighbors = _neighbors;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
Node* cloneGraph(Node* node) {
unordered_map<Node*, Node*> map;
return dfs(node, map);
}
private:
Node* dfs(Node* node, unordered_map<Node*, Node*>& map) {
if(map.find(node) != map.end()) return map[node];
Node* cloneNode = new Node(node->val, *(new vector<Node*>));
map[node] = cloneNode;
for(Node* neighbor : node->neighbors) {
cloneNode->neighbors.push_back(dfs(neighbor, map));
}
return cloneNode;
}
};
leetcode 200: 岛屿数量
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
class Solution {
public:
int numIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {
int rows = grid.size();
if(rows == 0) return 0;
int cols = grid[0].size();
if(cols == 0) return 0;
vector<vector<bool>> visited(rows, vector<bool>(cols, false));
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
if(grid[i][j] == '1' && !visited[i][j]) {
dfs(i, j, rows, cols, grid, visited);
res++;
}
}
}
return res;
}
private:
void dfs(int i, int j, int rows, int cols, vector<vector<char>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited) {
visited[i][j] = true;
if(i-1 >= 0 && grid[i-1][j] == '1' && !visited[i-1][j]) dfs(i-1, j, rows, cols, grid, visited);
if(i+1 < rows && grid[i+1][j] == '1' && !visited[i+1][j]) dfs(i+1, j, rows, cols, grid, visited);
if(j-1 >= 0 && grid[i][j-1] == '1' && !visited[i][j-1]) dfs(i, j-1, rows, cols, grid, visited);
if(j+1 < cols && grid[i][j+1] == '1' && !visited[i][j+1]) dfs(i, j+1, rows, cols, grid, visited);
}
};
leetcode 329: 矩阵中的最长递增路径
带缓存的DFS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
class Solution {
public:
int longestIncreasingPath(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
int rows = matrix.size();
if(rows == 0) return 0;
int cols = matrix[0].size();
if(cols == 0) return 0;
vector<vector<bool>> visited(rows, vector<bool>(cols, false));
vector<vector<int>> cache(rows, vector<int>(cols, -1));
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
if(cache[i][j] == -1) {
cache[i][j] = dfs(i, j, matrix, visited, cache, rows, cols);
res = max(res, cache[i][j]);
}
}
}
return res;
}
private:
int dfs(int i, int j, vector<vector<int>>& matrix, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, vector<vector<int>>& cache, int rows, int cols) {
if(cache[i][j] != -1) return cache[i][j];
cache[i][j] = 1;
visited[i][j] = true;
if(i-1 >= 0 && !visited[i-1][j] && matrix[i-1][j] > matrix[i][j]) cache[i][j] = max(cache[i][j], 1+dfs(i-1, j, matrix, visited, cache, rows, cols));
if(i+1 < rows && !visited[i+1][j] && matrix[i+1][j] > matrix[i][j]) cache[i][j] = max(cache[i][j], 1+dfs(i+1, j, matrix, visited, cache, rows, cols));
if(j-1 >= 0 && !visited[i][j-1] && matrix[i][j-1] > matrix[i][j]) cache[i][j] = max(cache[i][j], 1+dfs(i, j-1, matrix, visited, cache, rows, cols));
if(j+1 < cols && !visited[i][j+1] && matrix[i][j+1] > matrix[i][j]) cache[i][j] = max(cache[i][j], 1+dfs(i, j+1, matrix, visited, cache, rows, cols));
visited[i][j] = false;
return cache[i][j];
}
};
leetcode 207: 课程表
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
class Solution {
public:
bool canFinish(int numCourses, vector<vector<int>>& prerequisites) {
vector<vector<int>> graph(numCourses, vector<int>());
vector<int> indegree(numCourses, 0);
for(vector<int> prerequisite: prerequisites) {
int start = prerequisite[0];
int end = prerequisite[1];
graph[start].push_back(end);
indegree[end]++;
}
queue<int> q;
for(int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
if(indegree[i] == 0) {
q.push(i);
}
}
int cnt = 0;
while(!q.empty()) {
int node = q.front();
q.pop();
cnt++;
for(int neighbour: graph[node]) {
indegree[neighbour]--;
if(indegree[neighbour] == 0) {
q.push(neighbour);
}
}
}
return cnt == numCourses;
}
};
leetcode 210: 课程表II
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findOrder(int numCourses, vector<vector<int>>& prerequisites) {
vector<vector<int>> graph(numCourses, vector<int>());
vector<int> indegree(numCourses, 0);
for(vector<int> prerequisite: prerequisites) {
int start = prerequisite[1];
int end = prerequisite[0];
graph[start].push_back(end);
indegree[end]++;
}
vector<int> res;
queue<int> q;
for(int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
if(indegree[i] == 0) {
q.push(i);
}
}
while(!q.empty()) {
int node = q.front();
res.push_back(node);
q.pop();
for(int neighbour: graph[node]) {
indegree[neighbour]--;
if(indegree[neighbour] == 0) {
q.push(neighbour);
}
}
}
return res.size()==numCourses? res: vector<int>();
}
};
动态规划
leetcode 53: 最大连续子序列和
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
class Solution { public: int maxSubArray(vector<int>& nums) { if(nums.empty()) return 0; int maxSum = nums[0]; int maxHere = nums[0]; for(int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i++) { if(maxHere < 0) maxHere = 0; maxHere += nums[i]; maxSum = max(maxSum, maxHere); } return maxSum; } };
leetcode 62: 不同路径
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
class Solution { public: int uniquePaths(int m, int n) { vector<vector<int>> dp(m, vector<int>(n, 1)); for(int i = 1; i < m; i++) { for(int j = 1; j < n; j++) { dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] + dp[i][j-1]; } } return dp[m-1][n-1]; } };
leetcode 63: 不同路径II
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36
class Solution { public: int uniquePathsWithObstacles(vector<vector<int>>& obstacleGrid) { int m = obstacleGrid.size(); int n = obstacleGrid[0].size(); vector<vector<long>> dp(m, vector<long>(n, 1)); // int causes overflow if(obstacleGrid[0][0] == 1) { dp[0][0] = 0; } for(int i = 1; i < m; i++) { if(obstacleGrid[i][0] == 0) { dp[i][0] = dp[i-1][0]; } else { dp[i][0] = 0; } } for(int j = 1; j < n; j++) { if(obstacleGrid[0][j] == 0) { dp[0][j] = dp[0][j-1]; } else { dp[0][j] = 0; } } for(int i = 1; i < m; i++) { for(int j = 1; j < n; j++) { if(obstacleGrid[i][j] == 0) { dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] + dp[i][j-1]; } else { dp[i][j] = 0; } } } return dp[m-1][n-1]; } };
leetcode 64: 最小路径和
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
class Solution { public: int minPathSum(vector<vector<int>>& grid) { int m = grid.size(); int n = grid[0].size(); vector<vector<int>> dp(m, vector<int>(n, 0)); dp[0][0] = grid[0][0]; for(int i = 1; i < m; i++) { dp[i][0] = grid[i][0] + dp[i-1][0]; } for(int j = 1; j < n; j++) { dp[0][j] = grid[0][j] + dp[0][j-1]; } for(int i = 1; i < m; i++) { for(int j = 1; j < n; j++) { dp[i][j] = grid[i][j] + min(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1]); } } return dp[m-1][n-1]; } };
leetcode 72: 编辑距离
-
跟最长公共子序列比较
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27
class Solution { public: int minDistance(string word1, string word2) { int m = word1.length(); int n = word2.length(); int dp[m+1][n+1]; for(int i = 0; i <= m; i++) { dp[i][0] = i; } for(int j = 0; j <= n; j++) { dp[0][j] = j; } for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++) { if(word1[i-1] == word2[j-1]) dp[i][j] = min(min(dp[i-1][j-1], dp[i-1][j]+1), dp[i][j-1]+1); else dp[i][j] = min(min(dp[i-1][j-1]+1, dp[i-1][j]+1), dp[i][j-1]+1); } } for(int i = 0; i <= m; i++) { for(int j = 0; j <= n; j++) { cout << dp[i][j] << ' '; } cout << '\n'; } return dp[m][n]; } };
leetcode 91: 解码方法
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22
public class Solution { public int numDecodings(String s) { if(s == null || s.length() == 0) { return 0; } int n = s.length(); int[] dp = new int[n+1]; dp[0] = 1; dp[1] = s.charAt(0) != '0' ? 1 : 0; for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++) { int first = Integer.valueOf(s.substring(i-1, i)); int second = Integer.valueOf(s.substring(i-2, i)); if(first >= 1 && first <= 9) { dp[i] += dp[i-1]; } if(second >= 10 && second <= 26) { dp[i] += dp[i-2]; } } return dp[n]; } }
leetcode 120: 三角形最小路径和
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
class Solution { public: int minimumTotal(vector<vector<int>>& triangle) { int numRow = triangle.size(); vector<int> last(numRow, 0); vector<int> now(numRow, 0); now[0] = triangle[0][0]; for(int i = 1; i < numRow; i++) { last.swap(now); for(int j = 0; j < i+1; j++) { if(j == 0) { now[j] = last[j] + triangle[i][j]; } else if(j == i) { now[j] = last[j-1] + triangle[i][j]; } else { now[j] = min(last[j-1], last[j]) + triangle[i][j]; } } for(int i = 0; i < now.size(); i++) { cout<<now[i]<<" "; } cout<<endl; } int res = INT_MAX; for(int i = 0; i < now.size(); i++) { res = min(res, now[i]); } return res; } };
leetcode 152: 乘积最大子序列
思路:类似最大连续子序列和
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
class Solution {
public:
int maxProduct(vector<int>& nums) {
int res = nums[0];
int maxHere = res;
int minHere = res;
for(int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i++) {
if(nums[i] < 0) swap(maxHere, minHere);
maxHere = max(nums[i], nums[i] * maxHere);
minHere = min(nums[i], nums[i] * minHere);
res = max(res, maxHere);
}
return res;
}
};
leetcode 121: 买卖股票的最佳时机
-
方法1: 记录当前最小值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
int maxProfit(vector<int> &prices) { int maxPro = 0; int minPrice = INT_MAX; for(int i = 0; i < prices.size(); i++){ minPrice = min(minPrice, prices[i]); maxPro = max(maxPro, prices[i] - minPrice); } return maxPro; }
-
方法2: 最大连续子序列和
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
class Solution { public: int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) { int maxHere = 0; int maxSoFar = 0; for(int i = 1; i < prices.size(); i++) { if(maxHere < 0) maxHere = 0; maxHere += prices[i] - prices[i-1]; maxSoFar = max(maxSoFar, maxHere); } return maxSoFar; } };
leetcode 122: 买卖股票的最佳时机II
-
思路:只要涨就买
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
class Solution { public: int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) { int res = 0; for(int i = 1; i < prices.size(); i++) { int profit = prices[i] - prices[i-1]; if(profit > 0) { res += profit; } } return res; } };
leetcode 135: 分发糖果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
class Solution {
public:
int candy(vector<int>& ratings) {
vector<int> dpFromLeft(ratings.size(), 0);
vector<int> dpFromRight(ratings.size(), 0);
int cur;
for(int i = 0; i < ratings.size(); i++) {
if(i > 0 && ratings[i] > ratings[i-1]) cur++;
else cur = 1;
dpFromLeft[i] = cur;
}
for(int i = ratings.size()-1; i >= 0; i--) {
if(i < ratings.size()-1 && ratings[i] > ratings[i+1]) cur++;
else cur = 1;
dpFromRight[i] = cur;
}
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < ratings.size(); i++) {
res += max(dpFromLeft[i], dpFromRight[i]);
}
return res;
}
};
[leetcode 238: 除自身以外数组的乘积]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> productExceptSelf(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<int> left(nums.size(), 1);
vector<int> right(nums.size(), 1);
int product = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
left[i] = product;
product *= nums[i];
}
product = 1;
for(int i = nums.size()-1; i >= 0; i--) {
right[i] = product;
product *= nums[i];
}
vector<int> res(nums.size(), 0);
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
res[i] = left[i] * right[i];
}
return res;
}
};
leetcode 198: 打家劫舍
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
class Solution {
public:
int rob(vector<int>& nums) {
if(nums.empty()) return 0;
vector<int> dp(nums.size()+1, 0);
dp[1] = nums[0];
for(int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i++) {
dp[i+1] = max(dp[i], dp[i-1]+nums[i]);
}
return dp[nums.size()];
}
};
leetcode 279: 完全平方数
时间:$O(n^{1.5})$
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
class Solution {
public:
int numSquares(int n) {
vector<int> dp(n+1, INT_MAX);
vector<int> square;
for(long i = 1; i*i <= n; i++) {
dp[i*i] = 1;
square.push_back(i*i);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if(dp[i] == INT_MAX) {
for(int s: square) {
if(s >= i) break;
dp[i] = min(dp[i], dp[s]+dp[i-s]);
}
}
}
return dp[n];
}
};
leetcode 322: 零钱兑换
方法1:动态规划,时间$O(num_coins*amount)$
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
class Solution {
public:
int coinChange(vector<int>& coins, int amount) {
vector<int> dp(amount+1, INT_MAX);
dp[0] = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= amount; i++) {
for(int coin: coins) {
if(i-coin >= 0 && dp[i-coin] != INT_MAX) dp[i] = min(dp[i], dp[i-coin]+1);
}
}
return dp[amount]==INT_MAX? -1: dp[amount];
}
};
方法2:BFS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
class Solution {
public:
int coinChange(vector<int>& coins, int amount) {
if(amount == 0) return 0;
queue<int> q;
q.push(0);
unordered_set<int> set;
int step = 0;
while(!q.empty()) {
int size = q.size();
while(size--) {
int node = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int coin: coins) {
if(node+coin == amount) return step+1;
if(node+coin < amount && !set.count(node+coin)) {
q.push(node+coin);
set.insert(node+coin);
}
}
}
step++;
}
return -1;
}
};
leetcode 300: 最长上升子序列
方法1:动态规划,时间$O(n^2)$
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLIS(vector<int>& nums) {
if(nums.size() == 0) return 0;
vector<int> dp(nums.size(), 1);
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if(nums[i] > nums[j]) dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[j]+1);
}
}
int res = dp[0];
for(int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i++) {
res = max(res, dp[i]);
}
return res;
}
};
方法2:贪心+二分查找,时间$O(n\log n)$
我们维护一个数组 d[i] ,表示长度为 i 的最长上升子序列的末尾元素的最小值。
1
2
3
4
nums = [4,5,6,3]
len = 1 : [4], [5], [6], [3] => tails[0] = 3
len = 2 : [4, 5], [5, 6] => tails[1] = 5
len = 3 : [4, 5, 6] => tails[2] = 6
1
2
3
4
5
6
input: [0, 8, 4, 12, 2]
dp: [0]
dp: [0, 8]
dp: [0, 4]
dp: [0, 4, 12]
dp: [0, 2, 12]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLIS(vector<int>& nums) {
if(nums.size() == 0) return 0;
vector<int> dp(nums.size(), 0);
int len = 0;
for(int x: nums) {
int i = binarySearch(0, len-1, dp, x);
dp[i] = x;
if(i == len) len++;
}
return len;
}
private:
int binarySearch(int lo, int hi, vector<int>& dp, int target) {
while(lo <= hi) {
int mid = (lo + hi) / 2;
if(dp[mid] < target) lo = mid + 1;
else hi = mid - 1;
}
return lo;
}
};
leetcode 334: 递增的三元子序列
类似于tail数组
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
class Solution {
public:
bool increasingTriplet(vector<int>& nums) {
int small = INT_MAX;
int big = INT_MAX;
for(int num: nums) {
if(num <= small) small = num;
else if(num <= big) big = num;
else return true;
}
return false;
}
};
leetcode 221: 最大正方形
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
class Solution {
public:
int maximalSquare(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {
if (matrix.empty()) {
return 0;
}
int m = matrix.size(), n = matrix[0].size(), sz = 0;
vector<vector<int>> dp(m, vector<int>(n, 0));
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (!i || !j || matrix[i][j] == '0') {
dp[i][j] = matrix[i][j] - '0';
} else {
dp[i][j] = min(dp[i - 1][j - 1], min(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1])) + 1;
}
sz = max(dp[i][j], sz);
}
}
return sz * sz;
}
};
leetcode 85: 最大矩形
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
class Solution {public:
int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char> > &matrix) {
if(matrix.empty()) return 0;
const int m = matrix.size();
const int n = matrix[0].size();
int left[n], right[n], height[n];
fill_n(left,n,0); fill_n(right,n,n); fill_n(height,n,0);
int maxA = 0;
for(int i=0; i<m; i++) {
int cur_left=0, cur_right=n;
for(int j=0; j<n; j++) { // compute height (can do this from either side)
if(matrix[i][j]=='1') height[j]++;
else height[j]=0;
}
for(int j=0; j<n; j++) { // compute left (from left to right)
if(matrix[i][j]=='1') left[j]=max(left[j],cur_left);
else {left[j]=0; cur_left=j+1;}
}
// compute right (from right to left)
for(int j=n-1; j>=0; j--) {
if(matrix[i][j]=='1') right[j]=min(right[j],cur_right);
else {right[j]=n; cur_right=j;}
}
// compute the area of rectangle (can do this from either side)
for(int j=0; j<n; j++)
maxA = max(maxA,(right[j]-left[j])*height[j]);
}
return maxA;
}
};
剑指 Offer 14- I. 剪绳子
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
public class Solution {
public int cutRope(int target) {
if(target < 2) return -1;
int[] dp = new int[target+1];
dp[1] = 1;
for(int i = 2; i <= target; i++) {
dp[i] = 0;
for(int j = 1; j < i; j++) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], Math.max(dp[j], j)*(i-j));
}
}
return dp[target];
}
}
回溯
leetcode 17: 电话号码的字母组合
- 方法1:回溯
-
时间:$O(4^n)$
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23
class Solution { public: vector<string> letterCombinations(string digits) { vector<string> res; if(digits == "") return res; string comb; letterCombinations(digits, 0, comb, res); return res; } private: void letterCombinations(string digits, int cur, string comb, vector<string>& res) { if(cur == digits.length()) { res.push_back(comb); return; } vector<string> keys = {"", "", "abc", "def", "ghi", "jkl", "mno", "pqrs", "tuv", "wxyz"}; for(char c: keys[digits[cur] - '0']) { letterCombinations(digits, cur+1, comb+c, res); } } };
-
- 方法2:队列
-
时间:$O(4^n)$
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
class Solution { public: vector<string> letterCombinations(string digits) { vector<string> res; if(digits == "") return res; vector<string> keys = {"", "", "abc", "def", "ghi", "jkl", "mno", "pqrs", "tuv", "wxyz"}; queue<string> q; q.push(""); for(int i = 0; i < digits.size(); i++) { while(q.front().length() == i) { for(char c: keys[digits[i]-'0']) { q.push(q.front()+c); } q.pop(); } } while(!q.empty()) { res.push_back(q.front()); q.pop(); } return res; } };
-
leetcode 22: 括号生成
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
class Solution { public: vector<string> generateParenthesis(int n) { vector<string> ans; generateParenthesis(n, 0, "", ans); return ans; } void generateParenthesis(int open, int close, string res, vector<string> &ans) { if(open == 0 && close == 0) { ans.push_back(res); return; } if(open > 0) generateParenthesis(open - 1, close + 1, res + "(", ans); if(close > 0) generateParenthesis(open, close - 1, res + ")", ans); } };
leetcode 31: 下一个排列
-
方法1
-
从右往左扫描应该是先上升再下降,找到转折点left和right,将left指向的数与比它稍大的数交换,然后再将right后面的数排序。
-
时间:$O(n\log n)$
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22
class Solution { public: void nextPermutation(vector<int>& nums) { int size = nums.size(); if(size <= 1) return; int left = size-2; int right = size-1; while(left >= 0 && nums[left] >= nums[right]) { left--; right--; } if(left < 0) { sort(nums.begin(), nums.end()); } else { int i = size-1; while(i > right && nums[i] <= nums[left]) i--; swap(nums[left], nums[i]); sort(nums.begin()+right, nums.end()); } } };
-
-
方法2
-
思路:与上述方法相似,区别是排序改成翻转,因为最后一段总是逆序的,翻转后为顺序。
-
时间:$O(n)$
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22
class Solution { public: void nextPermutation(vector<int>& nums) { int size = nums.size(); if(size <= 1) return; int left = size-2; int right = size-1; while(left >= 0 && nums[left] >= nums[right]) { left--; right--; } if(left < 0) { reverse(nums.begin(), nums.end()); } else { int i = size-1; while(i > right && nums[i] <= nums[left]) i--; swap(nums[left], nums[i]); reverse(nums.begin()+right, nums.end()); } } };
-
leetcode 36: 有效的数独
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48
class Solution { public: bool isValidSudoku(vector<vector<char>>& board) { //row for(int i = 0; i < 9; i++) { int time[9] = {0}; for(int j = 0; j < 9; j++) { char c = board[i][j]; if(c != '.') { time[c - '1']++; if(time[c - '1'] >= 2) return false; } } } //column for(int i = 0; i < 9; i++) { int time[9] = {0}; for(int j = 0; j < 9; j++) { char c = board[j][i]; if(c != '.') { time[c - '1']++; if(time[c - '1'] >= 2) return false; } } } //sub-box int start[3] = {0, 3, 6}; for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++) for(int j = 0; j < 3; j++) { int startRow = start[i]; int startColumn = start[j]; int time[9] = {0}; for(int k = startRow; k < startRow + 3; k++) for(int l = startColumn; l < startColumn + 3; l++) { char c = board[k][l]; if(c != '.') { time[c - '1']++; if(time[c - '1'] >= 2) return false; } } } return true; } };
leetcode 37: 解数独
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49
class Solution { public: void solveSudoku(vector<vector<char>>& board) { solve(board); } private: bool solve(vector<vector<char>>& board) { int row, column; if(!findEmptyCell(board, row, column)) return true; for(int num = 1; num <= 9; num++) { if(noConflicts(board, row, column, num)) { board[row][column] = num + '0'; if(solve(board)) return true; board[row][column] = '.'; } } return false; } bool findEmptyCell(vector<vector<char>>& board, int& row, int& column) { for(int i = 0; i < 9; i++) for(int j = 0; j < 9; j++) if(board[i][j] == '.') { row = i; column = j; return true; } return false; } bool noConflicts(vector<vector<char>>& board, int row, int column, int num) { //row for(int i = 0; i < 9; i++) if(board[row][i] == num + '0') return false; //column for(int i = 0; i < 9; i++) if(board[i][column] == num + '0') return false; //sub-box int rowStart = row / 3 * 3; int columnStart = column / 3 * 3; for(int i = rowStart; i < rowStart + 3; i++) for(int j = columnStart; j < columnStart + 3; j++) { if(board[i][j] == num + '0') return false; } return true; } };
leetcode 51: N皇后
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42
class Solution { public: vector<vector<string>> solveNQueens(int n) { vector<vector<string>> res; vector<string> puzzle; for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { string row(n, '.'); puzzle.push_back(row); } backtrack(0, n, puzzle, res); return res; } private: void backtrack(int row, int n, vector<string>& puzzle, vector<vector<string>>& res) { if(row == n) { res.push_back(puzzle); return; } for(int col = 0; col < n; col++) { if(noConflicts(row, col, n, puzzle)) { puzzle[row][col] = 'Q'; backtrack(row+1, n, puzzle, res); puzzle[row][col] = '.'; } } } bool noConflicts(int row, int col, int n, vector<string>& puzzle) { for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if(puzzle[row][i] == 'Q') return false; if(puzzle[i][col] == 'Q') return false; if(puzzle[i][row+col-i] == 'Q') return false; if(puzzle[i][i-row+col] == 'Q') return false; } return true; } };
leetcode 52: N皇后II
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42
class Solution { public: int totalNQueens(int n) { int res = 0; vector<string> puzzle; for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { string row(n, '.'); puzzle.push_back(row); } backtrack(0, n, puzzle, res); return res; } private: void backtrack(int row, int n, vector<string>& puzzle, int& res) { if(row == n) { res++; return; } for(int col = 0; col < n; col++) { if(noConflicts(row, col, n, puzzle)) { puzzle[row][col] = 'Q'; backtrack(row+1, n, puzzle, res); puzzle[row][col] = '.'; } } } bool noConflicts(int row, int col, int n, vector<string>& puzzle) { for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if(puzzle[row][i] == 'Q') return false; if(puzzle[i][col] == 'Q') return false; if(puzzle[i][row+col-i] == 'Q') return false; if(puzzle[i][i-row+col] == 'Q') return false; } return true; } };
leetcode 60: 第k个排列
-
思路:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/permutation-sequence/solution/kang-tuo-bian-ma-by-rayyi-2/
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34
public class Solution { public String getPermutation(int n, int k) { int pos = 0; List<Integer> numbers = new ArrayList<>(); int[] factorial = new int[n+1]; StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); // create an array of factorial lookup int sum = 1; factorial[0] = 1; for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){ sum *= i; factorial[i] = sum; } // factorial[] = {1, 1, 2, 6, 24, ... n!} // create a list of numbers to get indices for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){ numbers.add(i); } // numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4} k--; for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){ int index = k/factorial[n-i]; sb.append(String.valueOf(numbers.get(index))); numbers.remove(index); k-=index*factorial[n-i]; } return String.valueOf(sb); } }
leetcode 39: 组合总和
-
题意:数组中数无重复,可以无限次使用。
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> combinationSum(vector<int>& candidates, int target) { vector<vector<int>> res; vector<int> combination; solve(candidates, target, 0, 0, combination, res); return res; } void solve(vector<int>& candidates, int target, int sum, int cur, vector<int>& combination, vector<vector<int>>& res) { if(sum == target) { res.push_back(combination); return; } if(sum > target) return; for(int i = cur; i < candidates.size(); i++) { combination.push_back(candidates[i]); solve(candidates, target, sum+candidates[i], i, combination, res); combination.pop_back(); } } };
leetcode 40: 组合总和II
-
题意:数组中数有重复,每个数只能用一次。结果中不能有重复。
-
思路:首次只能进入重复数字的第一个,用过第一个后才能进入第二个。
1 2 3
cur 1 1 1 2 3 i i i
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> combinationSum2(vector<int>& candidates, int target) { sort(candidates.begin(), candidates.end()); vector<vector<int>> res; vector<int> combination; solve(candidates, target, 0, 0, combination, res); return res; } void solve(vector<int>& candidates, int target, int sum, int cur, vector<int>& combination, vector<vector<int>>& res) { if(sum == target) { res.push_back(combination); return; } if(sum > target) return; for(int i = cur; i < candidates.size(); i++) { if(i > cur && candidates[i] == candidates[i-1]) continue; // avoid duplicates combination.push_back(candidates[i]); solve(candidates, target, sum+candidates[i], i+1, combination, res); combination.pop_back(); } } };
leetcode 46: 全排列
-
方法1:类似31题,next permutation
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> permute(vector<int>& nums) { vector<vector<int>> res; if(nums.size() <= 0) return res; sort(nums.begin(), nums.end()); res.push_back(nums); while(nextPermutation(nums)) { res.push_back(nums); } return res; } private: bool nextPermutation(vector<int>& nums) { int size = nums.size(); if(size <= 1) return false; int left = size-2; int right = size-1; while(left >= 0 && nums[left] >= nums[right]) { left--; right--; } if(left < 0) { reverse(nums.begin(), nums.end()); return false; } else { int i = size-1; while(i > right && nums[i] <= nums[left]) i--; swap(nums[left], nums[i]); reverse(nums.begin()+right, nums.end()); } return true; } };
-
-
方法2:回溯
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> permute(vector<int>& nums) { vector<vector<int>> res; if(nums.size() <= 0) return res; vector<int> combination; vector<bool> available; for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) { available.push_back(true); } backtrack(0, nums.size(), nums, available, combination, res); return res; } private: void backtrack(int cur, int size, vector<int>& nums, vector<bool>& available, vector<int>& combination, vector<vector<int>>& res) { if(cur == size) { res.push_back(combination); return; } for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) { if(available[i]) { combination.push_back(nums[i]); available[i] = false; backtrack(cur+1, size, nums, available, combination, res); combination.pop_back(); available[i] = true; } } } };
-
leetcode 47: 全排列II
-
题意:跟前面一题的区别是给的数有重复,但是结果不能有重复。
-
方法1:与前一题方法1相同。
-
方法2:回溯
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> permuteUnique(vector<int>& nums) { vector<vector<int>> res; if(nums.size() <= 0) return res; vector<int> combination; vector<bool> available; for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) { available.push_back(true); } sort(nums.begin(), nums.end()); backtrack(0, nums.size(), nums, available, combination, res); return res; } private: void backtrack(int cur, int size, vector<int>& nums, vector<bool>& available, vector<int>& combination, vector<vector<int>>& res) { if(cur == size) { res.push_back(combination); return; } for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) { if(i >= 1 && nums[i] == nums[i-1] && available[i-1]) continue; // avoid duplicates if(available[i]) { combination.push_back(nums[i]); available[i] = false; backtrack(cur+1, size, nums, available, combination, res); combination.pop_back(); available[i] = true; } } } };
-
leetcode 78: 子集
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> subsets(vector<int>& nums) { vector<vector<int>> res; vector<int> combination; vector<bool> available; for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) { available.push_back(true); } backtrack(0, nums.size(), nums, combination, available, res); return res; } private: void backtrack(int cur, int size, vector<int>& nums, vector<int>& combination, vector<bool>& available, vector<vector<int>>& res) { res.push_back(combination); for(int i = cur; i < size; i++) { if(available[i]) { combination.push_back(nums[i]); available[i] = false; backtrack(i+1, size, nums, combination, available, res); combination.pop_back(); available[i] = true; } } } };
leetcode 90: 子集II
-
题意:跟前面一题的区别是给的数有重复,但是结果不能有重复。
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> subsetsWithDup(vector<int>& nums) { vector<vector<int>> res; vector<int> combination; vector<bool> available; for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) { available.push_back(true); } sort(nums.begin(), nums.end()); backtrack(0, nums.size(), nums, combination, available, res); return res; } private: void backtrack(int cur, int size, vector<int>& nums, vector<int>& combination, vector<bool>& available, vector<vector<int>>& res) { res.push_back(combination); for(int i = cur; i < size; i++) { if(i > cur && nums[i] == nums[i-1] && available[i-1]) continue; if(available[i]) { combination.push_back(nums[i]); available[i] = false; backtrack(i+1, size, nums, combination, available, res); combination.pop_back(); available[i] = true; } } } };
leetcode 93: 复原IP地址
-
方法1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34
class Solution { public: vector<string> restoreIpAddresses(string s) { vector<string> res; vector<int> pos; backtrack(0, pos, s, res); return res; } private: void backtrack(int cur, vector<int>& pos, string& s, vector<string>& res) { if(pos.size() == 3 && s.length()-cur >= 1 && s.length()-cur <= 3 && atoi(s.substr(cur, s.length()-cur).c_str()) < 256 && !(s.length()-cur > 1 && s[cur] == '0')) { string ip = s.substr(0, pos[0]) + '.'; ip += s.substr(pos[0], pos[1]-pos[0]) + '.'; ip += s.substr(pos[1], pos[2]-pos[1]) + '.'; ip += s.substr(pos[2], s.length()-pos[2]+1); res.push_back(ip); return; } if(cur >= s.length() || pos.size() > 3) { return; } for(int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) { if(atoi(s.substr(cur, i).c_str()) < 256 && !(i > 1 && s[cur] == '0')) { pos.push_back(cur+i); backtrack(cur+i, pos, s, res); pos.pop_back(); } } } };
-
方法2
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
// https://leetcode.com/problems/restore-ip-addresses/discuss/30972/WHO-CAN-BEAT-THIS-CODE vector<string> restoreIpAddresses(string s) { vector<string> ret; string ans; for (int a=1; a<=3; a++) { for (int b=1; b<=3; b++) { for (int c=1; c<=3; c++) { for (int d=1; d<=3; d++) { if (a+b+c+d == s.length()) { int A = stoi(s.substr(0, a)); int B = stoi(s.substr(a, b)); int C = stoi(s.substr(a+b, c)); int D = stoi(s.substr(a+b+c, d)); if (A<=255 && B<=255 && C<=255 && D<=255) if ( (ans=to_string(A)+"."+to_string(B)+"."+to_string(C)+"."+to_string(D)).length() == s.length()+3) ret.push_back(ans); } } } } } return ret; }
leetcode 95: 不同的二叉排序树II
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: vector<TreeNode*> generateTrees(int n) { vector<TreeNode*> result; if(n <= 0) return result; return genTrees(1, n); } private: vector<TreeNode*> genTrees(int start, int end) { vector<TreeNode*> v; if(start > end) { v.push_back(NULL); return v; } for(int i = start; i <= end; i++) { vector<TreeNode*> left = genTrees(start, i-1); vector<TreeNode*> right = genTrees(i+1, end); for(TreeNode* leftNode: left) { for(TreeNode* rightNode: right) { TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(i); root->left = leftNode; root->right = rightNode; v.push_back(root); } } } return v; } };
leetcode 96: 不同的二叉排序树
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34
/* * a[n] = a[0] * a[n-1] * + a[1] * a[n-2] * + ... * + a[n-1] * a[0] */ class Solution { public: int numTrees(int n) { int trees[n+1] = {0}; trees[0] = 1; for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { for(int j = 0; j < i; j++) { trees[i] += trees[j] * trees[i-j-1]; } } return trees[n]; } }; /* * catalan[n] = C(n, 2n) / (n+1) * catalan[n] / catalan[n-1] = 2 * (2n-1) / (n+1) */ class Solution { public: int numTrees(int n) { long catalan = 1; for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { catalan = catalan * 2 * (2 * i - 1) / (i + 1); } return catalan; } };
BFS
leetcode 126: 单词接龙II
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<string>> findLadders(string beginWord, string endWord, vector<string>& wordList) {
unordered_set<string> set(wordList.begin(), wordList.end());
queue<vector<string>> q;
q.push(vector<string>{beginWord});
vector<vector<string>> res;
int step = 1;
while(!q.empty() && res.empty()) {
int size = q.size();
vector<string> wordsToBeRemoved;
while(size--) {
vector<string> vec = q.front();
q.pop();
string word = vec.back();
if(word == endWord) {
res.push_back(vec);
}
for(int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
char c = word[i];
for(int j = 'a'; j <= 'z'; j++) {
word[i] = j;
if(set.count(word)) {
vec.push_back(word);
q.push(vec);
vec.pop_back();
wordsToBeRemoved.push_back(word);
}
}
word[i] = c;
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < wordsToBeRemoved.size(); i++) {
set.erase(wordsToBeRemoved[i]);
}
step++;
}
return res;
}
};
leetcode 127: 单词接龙
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
class Solution {
public:
int ladderLength(string beginWord, string endWord, vector<string>& wordList) {
unordered_set<string> set(wordList.begin(), wordList.end());
queue<string> q;
q.push(beginWord);
int step = 1;
while(!q.empty()) {
int size = q.size();
while(size--) {
string word = q.front();
q.pop();
if(word == endWord) return step;
for(int i = 0; i < word.size(); i++) {
char c = word[i];
for(char j = 'a'; j <= 'z'; j++) {
word[i] = j;
if(set.count(word)) {
q.push(word);
set.erase(word);
}
}
word[i] = c;
}
}
step++;
}
return 0;
}
};
数学
leetcode 7: 整数反转
-
需要判断int类型的整数是否溢出,方法是将可能溢出的数还原比较是否与原先的数相等,或者用long类型
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22
class Solution { public: int reverse(int x) { //bool isPositive = true; //if(x < 0) { // isPositive = false; // x = -x; //} int result = 0; while(x != 0) { int tail = x % 10; int newResult = 10 * result + tail; if((newResult - tail) / 10 != result) return 0; result = newResult; x = x / 10; } //if(!isPositive) // result = - result; return result; } };
leetcode 29: 两数相除
-
思路:位操作
15/3,除数利用加法倍增,直到大于被除数,3«2=12,所以结果至少为1«2=4. 问题转化为3/3.
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26
class Solution { public: int divide(int dividend, int divisor) { if(dividend < 0 && divisor == 0) return INT_MIN; if(dividend > 0 && divisor == 0) return INT_MAX; if(dividend == INT_MIN && divisor == -1) return INT_MAX; int result = 0; bool isPositive = true; if((dividend < 0 && divisor > 0) || (dividend > 0 && divisor < 0)) isPositive = false; long long dvd = labs(dividend); long long dvs = labs(divisor); while(dvd >= dvs) { long long tmp = dvs; int times = 1; while(dvd >= tmp + tmp) { tmp = tmp + tmp; times = times + times; } result = result + times; dvd = dvd - tmp; } if(!isPositive) return -result; return result; } };
-
leetcode 43: 字符串相乘
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59
class Solution { public: string multiply(string num1, string num2) { string res = "0"; for(int i = num2.length()-1; i >= 0; i--) { string prod = multiply(num1, num2[i]); for(int j = 0; j < num2.length()-1-i; j++) { prod += '0'; } res = add(res, prod); } int i = 0; while(i < res.length()-1 && res[i] == '0') i++; return res.substr(i, res.length()-i); } private: string multiply(string num1, char num2) { string res; int carry = 0; for(int i = num1.length()-1; i >= 0; i--) { int prod = (num1[i]-'0') * (num2-'0') + carry; carry = prod / 10; res = char(prod % 10 + '0') + res; } if(carry) { res = char(carry + '0') + res; } return res; } string add(string num1, string num2) { string res; int carry = 0; int len1 = num1.length(); int len2 = num2.length(); for(int i = 0; i < max(len1, len2); i++) { int sum = carry; if(len1-1-i >= 0) { sum += num1[num1.length()-1-i] - '0'; } if(len2-1-i >= 0) { sum += num2[num2.length()-1-i] - '0'; } carry = sum / 10; res = char(sum % 10 + '0') + res; } if(carry) { res = char(carry + '0') + res; } return res; } };
leetcode 50: Pow(w, n)
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
class Solution { public: double myPow(double x, int n) { return pow(x, n); } private: double pow(double x, long n) { if(n == 0) return 1; if(n < 0) return 1 / pow(x, -n); if(n % 2) return pow(x*x, n/2) * x; return pow(x*x, n/2); } };
leetcode 65: 有效数字
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103
class Solution { public: bool isNumber(string s) { /* "0" => true " 0.1 " => true "abc" => false "1 a" => false "2e10" => true " -90e3 " => true " 1e" => false "e3" => false " 6e-1" => true " 99e2.5 " => false "53.5e93" => true " --6 " => false "-+3" => false "95a54e53" => false "." => false ". 1" => false ".-4" "6e6.5" */ // remove space of two sides int start = 0; int end = s.length(); while(start < s.length()) { if(s[start] == ' ') start++; else break; } while(end > 0) { if(s[end-1] == ' ') end--; else break; } s = s.substr(start, end-start); // exp size_t exp_pos = s.find('e'); if(exp_pos != string::npos) { string num1 = s.substr(0, exp_pos); string num2 = s.substr(exp_pos+1, s.size()-exp_pos-1); if(isValid(num1) && isInt(num2)) return true; } else { if(isValid(s)) return true; } return false; } private: bool isValid(string s) { cout << "#" << s << "#"; // empty if(s == "") return false; // alpha for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) { if(isalpha(s[i]) || s[i] == ' ') return false; } // negtive, positive, point int num_pos_neg = 0; int num_point = 0; int num_digit = 0; for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) { if(isdigit(s[i])) num_digit++; else if(s[i] == '.') num_point++; else if(s[i] == '+' || s[i] == '-') { num_pos_neg++; if(num_digit > 0 || num_point > 0) return false; } } if(num_pos_neg > 1 || num_point > 1 || num_digit == 0) return false; return true; } bool isInt(string s) { cout << "#" << s << "#"; // empty if(s == "") return false; // alpha for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) { if(isalpha(s[i]) || s[i] == ' ') return false; } // negtive, positive, point int num_pos_neg = 0; int num_point = 0; int num_digit = 0; for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) { if(isdigit(s[i])) num_digit++; else if(s[i] == '.') num_point++; else if(s[i] == '+' || s[i] == '-') { num_pos_neg++; if(num_digit > 0 || num_point > 0) return false; } } if(num_pos_neg > 1 || num_point > 0 || num_digit == 0) return false; return true; } };
leetcode 69: x的平方根
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
class Solution { public: int mySqrt(int x) { if(x < 0) return -1; if(x == 0) return 0; int lo = 1; int hi = x; while(lo <= hi) { int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2; // avoid overflow when (lo + hi) / 2 if(mid == x/mid) return mid; // avoid overflow when mid*mid else if(mid < x/mid) lo = mid + 1; else hi = mid - 1; } return hi; } };
leetcode 166: 分数到小数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
class Solution {
public:
string fractionToDecimal(int numerator, int denominator) {
if(numerator == 0) return "0";
// sign
string res;
if((numerator > 0) ^ (denominator > 0)) res += "-";
long absNumerator = abs((long)numerator);
long absDenominator = abs((long)denominator);
// integral part
res += to_string(absNumerator / absDenominator);
long remainder = absNumerator % absDenominator;
if(remainder == 0) return res;
// fractional part
res += '.';
unordered_map<long, int> map;
while(remainder != 0) {
if(map.count(remainder)) {
res.insert(map[remainder], "(");
res += ')';
break;
}
map[remainder] = res.length();
remainder *= 10;
res += to_string(remainder / absDenominator);
remainder = remainder % absDenominator;
}
return res;
}
};
leetcode 171: 阶乘后的零
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
class Solution {
public:
int trailingZeroes(int n) {
int res = 0;
while(n != 0) {
res += n/5;
n /= 5;
}
return res;
}
};
leetcode 179: 最大数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
class Solution {
public:
string largestNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end(), [](int& a, int& b){ return to_string(a)+to_string(b) > to_string(b)+to_string(a); });
string res;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
res += to_string(nums[i]);
}
while(res[0] == '0') {
res.erase(0, 1);
}
return res.empty()? "0": res;
}
};
leetcode 190: 颠倒二进制位
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
uint32_t reverseBits(uint32_t n) {
uint32_t count=0;
int i;
for(i=0;i<32;i++){
count=count*2+n%2;
n=n/2;
}
return count;
}
leetcode 204: 计数质数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
class Solution {
public:
int countPrimes(int n) {
int res = 0;
vector<bool> isPrime(n, true);
for(long i = 2; i < n; i++) {
if(isPrime[i]) {
res++;
for(long j = i*i; j < n; j += i) {
isPrime[j] = false;
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
leetcode 371: 两整数之和
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
class Solution {
public:
int getSum(int a, int b) {
while(b != 0) {
unsigned int carry = a & b;
a = a ^ b;
b = carry << 1;
}
return a;
}
};
剑指 Offer 43. 1~n整数中1出现的次数
思路:找规律,分三种情况当前位是0、当前位是1、当前位大于1三种情况。
- 当前位是0: 2304, 0010~2219, 000~229, 23*10
- 当前位是1: 2314, 0010~2314, 000~234, 23*10+4+1
- 当前位大于1: 2344, 0010~2319, 000~239, (23+1)*10
剑指 Offer 44. 数字序列中某一位的数字
思路:找规律
- 1~9: 1位*9个数
- 10~99: 2位*90个数
- 100~999: 3位*900个数
剑指 Offer 49. 丑数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
public class Solution {
public int GetUglyNumber_Solution(int index) {
// 1 2 3 4
// 2: 2 4 6 8
// 3: 3 6 9 12
// 5: 5 10 15 20
if (index == 0) return 0;
List<Integer> uglyNumbers = new ArrayList<>();
int p2 = 0;
int p3 = 0;
int p5 = 0;
int newNum = 1;
uglyNumbers.add(newNum);
while (uglyNumbers.size() < index) {
newNum = Math.min(Math.min(uglyNumbers.get(p2)*2, uglyNumbers.get(p3)*3), uglyNumbers.get(p5)*5);
if (newNum == uglyNumbers.get(p2)*2) p2++;
if (newNum == uglyNumbers.get(p3)*3) p3++;
if (newNum == uglyNumbers.get(p5)*5) p5++;
uglyNumbers.add(newNum);
}
return uglyNumbers.get(index-1);
}
}
剑指 Offer 60. n个骰子的点数
思路:基于循环求骰子点数
剑指 Offer 64. 求1+2+…+n
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
public class Solution {
public int Sum_Solution(int n) {
int res = n;
boolean flag = (res > 0) && ((res += Sum_Solution(n-1)) > 0);
return res;
}
}
剑指 Offer 62. 圆圈中最后剩下的数字
推导:
根据规律
k+1->0
k+2->1
…
n-1->n-k-2
0->n-k-1
1->n-k
…
k-1->n-2
所以$p(x)=(x-k-1)\%n$
$p^{-1}(x)=(x+k+1)\%n$
因为$k=(m-1)\%n$
所以$f(n,m)$
$=f’(n-1,m)$
$=p^{-1}[f(n-1,m)]$
$=[f(n-1,m)+k+1]\%n$
$=[f(n-1,m)+m]\%n$
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
public class Solution {
public static int LastRemaining_Solution(int n, int m) {
if (n <= 0 || m <= 0) return -1;
int last = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
last = (last + m) % i;
}
return last;
}
}
并发
leetcode 1114: 按序打印
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34
import java.util.concurrent.*; class Foo { Semaphore run2, run3; public Foo() { run2 = new Semaphore(0); run3 = new Semaphore(0); } public void first(Runnable printFirst) throws InterruptedException { // printFirst.run() outputs "first". Do not change or remove this line. printFirst.run(); run2.release(); } public void second(Runnable printSecond) throws InterruptedException { run2.acquire(); // printSecond.run() outputs "second". Do not change or remove this line. printSecond.run(); run3.release(); } public void third(Runnable printThird) throws InterruptedException { run3.acquire(); // printThird.run() outputs "third". Do not change or remove this line. printThird.run(); } }
leetcode 1115: 交替打印FooBar
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35
import java.util.concurrent.*; class FooBar { Semaphore foo = new Semaphore(1); Semaphore bar = new Semaphore(0); private int n; public FooBar(int n) { this.n = n; } public void foo(Runnable printFoo) throws InterruptedException { for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { foo.acquire(); // printFoo.run() outputs "foo". Do not change or remove this line. printFoo.run(); bar.release(); } } public void bar(Runnable printBar) throws InterruptedException { for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { bar.acquire(); // printBar.run() outputs "bar". Do not change or remove this line. printBar.run(); foo.release(); } } }
leetcode 1116: 打印零与奇偶数
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41
import java.util.concurrent.*; class ZeroEvenOdd { Semaphore zero = new Semaphore(1); Semaphore even = new Semaphore(0); Semaphore odd = new Semaphore(0); private int n; public ZeroEvenOdd(int n) { this.n = n; } // printNumber.accept(x) outputs "x", where x is an integer. public void zero(IntConsumer printNumber) throws InterruptedException { for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { zero.acquire(); printNumber.accept(0); if(i % 2 == 1) { odd.release(); } else { even.release(); } } } public void even(IntConsumer printNumber) throws InterruptedException { for(int i = 2; i <= n; i += 2) { even.acquire(); printNumber.accept(i); zero.release(); } } public void odd(IntConsumer printNumber) throws InterruptedException { for(int i = 1; i <= n; i += 2) { odd.acquire(); printNumber.accept(i); zero.release(); } } }
leetcode 1117: H20生成
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
import java.util.concurrent.*; class H2O { Semaphore h; Semaphore o; public H2O() { h = new Semaphore(2); o = new Semaphore(0); } public void hydrogen(Runnable releaseHydrogen) throws InterruptedException { h.acquire(); // releaseHydrogen.run() outputs "H". Do not change or remove this line. releaseHydrogen.run(); o.release(); } public void oxygen(Runnable releaseOxygen) throws InterruptedException { o.acquire(2); // releaseOxygen.run() outputs "O". Do not change or remove this line. releaseOxygen.run(); h.release(2); } }
leetcode 1195: 交替打印字符串
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70
import java.util.concurrent.*; class FizzBuzz { private int n; Semaphore number; Semaphore fizz; Semaphore buzz; Semaphore fizzbuzz; public FizzBuzz(int n) { this.n = n; number = new Semaphore(1); fizz = new Semaphore(0); buzz = new Semaphore(0); fizzbuzz = new Semaphore(0); } // printFizz.run() outputs "fizz". public void fizz(Runnable printFizz) throws InterruptedException { for(int i = 3; i <= n; i += 3) { if(i % 5 != 0) { fizz.acquire(); printFizz.run(); // System.out.println("fizz"+i); number.release(); } } } // printBuzz.run() outputs "buzz". public void buzz(Runnable printBuzz) throws InterruptedException { for(int i = 5; i <= n; i += 5) { if(i % 3 != 0) { buzz.acquire(); printBuzz.run(); // System.out.println("buzz"+i); number.release(); } } } // printFizzBuzz.run() outputs "fizzbuzz". public void fizzbuzz(Runnable printFizzBuzz) throws InterruptedException { for(int i = 15; i <= n; i += 15) { fizzbuzz.acquire(); printFizzBuzz.run(); // System.out.println("fizzbuzz"+i); number.release(); } } // printNumber.accept(x) outputs "x", where x is an integer. public void number(IntConsumer printNumber) throws InterruptedException { for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { number.acquire(); if(i % 3 != 0 && i % 5 != 0) { printNumber.accept(i); // System.out.println(i); number.release(); } else if(i % 15 == 0) { fizzbuzz.release(); } else if(i % 3 == 0) { fizz.release(); } else if(i % 5 == 0) { buzz.release(); } } } }
抢票
-
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67
// 某场演唱会门票1000张(票面编号0-999),落入了黄牛A、B、C手中, // 三人同时对外售票(按编号顺序卖票),票价500/张,总票数每卖掉100张,每张票涨价100元。 // 请编写出程序,最终打印出三个人卖掉每张票的编号和每人的总收入。 import java.util.ArrayList; class TicketSeller implements Runnable { private static volatile int ticketNum = 0; private static int ticketPrice = 500; private ArrayList<Integer> tickets = new ArrayList<>(); private int profit = 0; @Override public void run() { while(ticketNum < 1000) { synchronized(TicketSeller.class) { profit += ticketPrice; tickets.add(ticketNum++); ticketPrice = 500 + ticketNum / 100 * 100; } } System.out.println(String.valueOf(tickets.size()) + " " + profit + " " + tickets); } public static void main(String[] args) { Thread a = new Thread(new TicketSeller()); Thread b = new Thread(new TicketSeller()); Thread c = new Thread(new TicketSeller()); a.start(); b.start(); c.start(); } } import java.util.ArrayList; class TicketSeller implements Runnable { private volatile int ticketNum = 0; private int ticketPrice = 500; @Override public void run() { ArrayList<Integer> tickets = new ArrayList<>(); int profit = 0; while(ticketNum < 1000) { synchronized(TicketSeller.class) { profit += ticketPrice; tickets.add(ticketNum++); ticketPrice = 500 + ticketNum / 100 * 100; } } System.out.println(tickets); System.out.println(profit); } public static void main(String[] args) { TicketSeller ticketSeller = new TicketSeller(); Thread a = new Thread(ticketSeller); Thread b = new Thread(ticketSeller); Thread c = new Thread(ticketSeller); a.start(); b.start(); c.start(); } }
FooBar
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FooBar fooBar = new FooBar(10);
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
fooBar.foo();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
fooBar.bar();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
}
class FooBar {
private Semaphore foo = new Semaphore(1);
private Semaphore bar = new Semaphore(0);
private int n;
public FooBar(int n) {
this.n = n;
}
public void foo() throws InterruptedException {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
foo.acquire();
System.out.println("foo");
bar.release();
}
}
public void bar() throws InterruptedException {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
bar.acquire();
System.out.println("bar");
foo.release();
}
}
}
生产者消费者
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProducerConsumer producerConsumer = new ProducerConsumer(5);
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
producerConsumer.produce();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
producerConsumer.consume();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
}
class ProducerConsumer {
public ProducerConsumer(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
count = 0;
mutex = new Semaphore(1);
empty = new Semaphore(capacity);
full = new Semaphore(0);
}
private int capacity;
private int count;
private Semaphore mutex;
private Semaphore empty;
private Semaphore full;
public void produce() throws InterruptedException {
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
empty.acquire();
mutex.acquire();
System.out.println("produce" + String.valueOf(count++));
mutex.release();
full.release();
}
}
public void consume() throws InterruptedException {
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
full.acquire();
mutex.acquire();
System.out.println("consume" + count--);
mutex.release();
empty.release();
}
}
}
死锁
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
public class Main {
private static String a = "a";
private static String b = "b";
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (a) {
try {
Thread.currentThread().sleep(2000);
synchronized (b) {
System.out.println(1);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (b) {
try {
Thread.currentThread().sleep(2000);
synchronized (a) {
System.out.println(2);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
实现一个k-v的内存计数类,功能包括添加、删除、查询、自增四个功能
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
class KV {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
synchronized void add(int key) {
map.putIfAbsent(key, 0);
}
synchronized void delete(int key) {
map.remove(key);
}
synchronized int get(int key) {
return map.get(key);
}
synchronized void increment(int key) {
map.put(key, map.getOrDefault(key, 0) + 1);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
class KV {
Map<Integer, AtomicInteger> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
void add(int key) {
map.putIfAbsent(key, new AtomicInteger(0));
}
synchronized void delete(int key) {
map.remove(key);
}
synchronized int get(int key) {
return map.get(key).get();
}
void increment(int key) {
map.get(key).getAndIncrement();
}
}
SQL
leetcode 175: 组合两个表
1
2
3
SELECT Person.FirstName, Person.LastName, Address.City, Address.State
FROM Person
LEFT JOIN Address ON Person.PersonId = Address.PersonId;
leetcode 176: 第二高的薪水
1
SELECT (SELECT DISTINCT Salary FROM Employee ORDER BY Salary DESC LIMIT 1 OFFSET 1) AS SecondHighestSalary
1
SELECT max(Salary) AS SecondHighestSalary FROM Employee WHERE Salary < (SELECT max(Salary) FROM Employee)
leetcode 177: 第N高的薪水
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
CREATE FUNCTION getNthHighestSalary(N INT) RETURNS INT
BEGIN
DECLARE M INT;
SET M=N-1;
RETURN (
# Write your MySQL query statement below.
SELECT(SELECT DISTINCT Salary FROM Employee ORDER BY Salary DESC LIMIT 1 OFFSET M) AS `getNthHighestSalary(2)`
);
END
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
CREATE FUNCTION getNthHighestSalary(N INT) RETURNS INT
BEGIN
DECLARE M INT;
SET M=N-1;
RETURN (
# Write your MySQL query statement below.
SELECT DISTINCT Salary AS `getNthHighestSalary(2)` FROM Employee ORDER BY Salary DESC LIMIT 1 OFFSET M
);
END
leetcode 178: 分数排名
1
2
3
4
SELECT
Score,
(SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT Score) FROM Scores WHERE Score >= s.Score) AS Rank
FROM Scores AS s ORDER BY Score DESC
leetcode 180: 连续出现的数字
1
2
3
SELECT DISTINCT l1.Num AS ConsecutiveNums FROM Logs AS l1, Logs AS l2, Logs AS l3
WHERE l1.Id = l2.Id-1 AND l1.id = l3.Id-2
AND l1.Num=l2.Num AND l1.Num=l3.Num
leetcode 181: 超过经理收入的员工
1
2
3
4
SELECT a.Name AS Employee
FROM Employee AS a
JOIN Employee AS b ON a.managerId = b.Id
WHERE a.Salary > b.Salary


